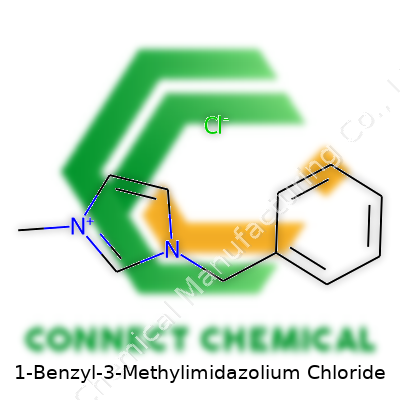
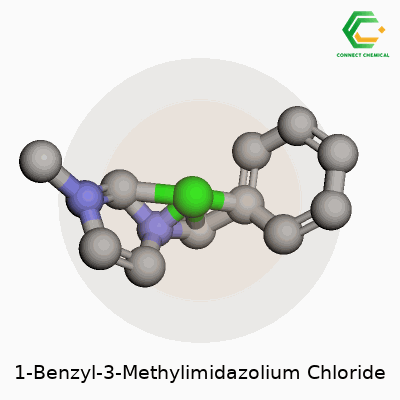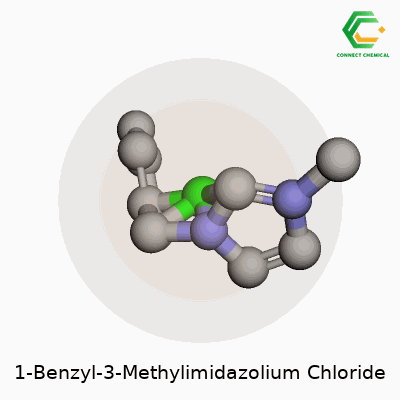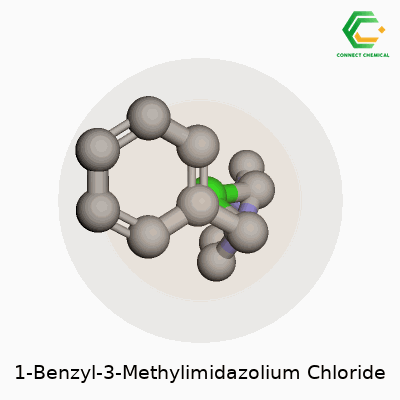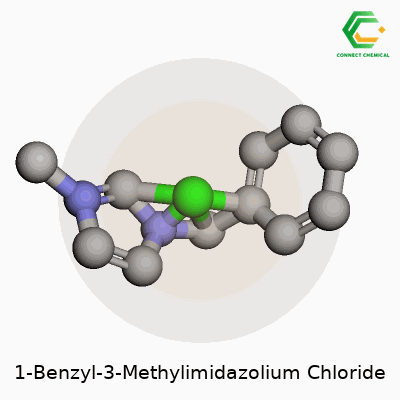
1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride: A Detailed Look
Historical Development
Before the new century, most folks in the chemical industry hadn’t looked much beyond common salts for solvents or reaction media. Old-school technology steered clear of anything with an unpronounceable name. Near the turn of the millennium, things looked different. New green chemistry needed materials that broke the mold. Imidazolium-based ionic liquids, especially 1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride (BzmimCl), came off the backbench and into the lab spotlight. Researchers saw this salt offering unique solvent options with lower volatility, and pharmaceutical companies gave it attention as a way around some old toxic reagents. Chatter about ionic liquids snowballed through journals and trade shows in the early 2000s.
Product Overview
People know 1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride mainly as a room-temperature ionic liquid. In plain terms, it’s a salt that doesn’t need a high oven to melt. Instead, it starts out as a solid and can turn into a viscous liquid near human body temperature, making it easier to store, ship, and handle compared to most flammable solvents. Chemists run to it because of its strong solvating power and wide chemical compatibility—sometimes, it enables reactions that regular water or organic solvents simply can’t touch. Manufacturers usually pack it in airtight containers to keep it from taking on water, since it loves to soak up moisture from the air.
Physical & Chemical Properties
BzmimCl goes on a short list of salts that melt below 100°C. Its melting point lands around 65°C, but the actual value leans on how fresh and dry the batch is. The compound’s structure keeps it both stable and highly polar, letting it carry out some unusual tricks in the lab. Under normal conditions, it looks like a white or pale yellow crystalline powder, turning syrupy as it warms up. It dissolves well in water, DMSO, and even some alcohols, setting it miles apart from plain sodium chloride. Its ability to act as a solvent for metal ions, organic molecules, or even whole enzymes means it lets researchers and engineers tweak reaction outcomes or speed up old, slow processes with better yields.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Suppliers tend to label this product clear and straightforward so folks know what they're getting. Names in industry follow IUPAC—1-Benzyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride, BzmimCl, or sometimes Benzylmethylimidazolium chloride. Labels list purity—most common grades hit at least 98%—and show the CAS number so buyers can check for regulatory status or shipping paperwork. Packing sizes run from grams for university labs to kilos for bigger process lines. Labels warn about water content because humidity changes its character. During storage, keeping it dry and in airtight conditions makes a world of difference in quality and shelf life.
Preparation Method
Lab work to produce BzmimCl usually starts with methylimidazole and benzyl chloride. Methylimidazole reacts in excess with benzyl chloride in a simple substitution reaction. Stirring at mild heat for a few hours turns the hot mixture into a goopy intermediate, then crystallizes out as things cool down and the byproducts get washed away. Purification comes by repeated recrystallization from a polar solvent, often ethanol, or washing with ethyl acetate. In industry, folks scale this up with bigger glassware and fancier vacuum systems, but the chemistry stays the same. Anyone making it for sale keeps close track of residual benzyl chloride because of toxicity risks. Drying under vacuum rounds out the process.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
BzmimCl doesn’t just act as a simple solvent. Chemists use it as a reaction partner in ion exchange to create other imidazolium salts—swap the chloride for tetrafluoroborate, for example, and make a new room-temperature ionic liquid. Its imidazolium core gives it a shot at catalyzing certain organic reactions on its own. In some cases, a tweak to the benzyl group or a switch in alkyl groups on the imidazole opens new doors and shifts its behavior. Teams in research often use BzmimCl to stabilize nanoparticles, dissolve cellulose fibers for making biomass plastics, or coax tricky reactions in organic synthesis that flop in regular solvents.
Synonyms & Product Names
Ask around different labs or suppliers, and this chemical picks up a handful of alternatives. Trade catalogs list it as BzmimCl, benzylmethylimidazolium chloride, or the full IUPAC name. Some brands shorten it further, but the basic formula—C11H13N2Cl—always stays the same. Universities and chemical manufacturers may give it a catalog code for their own ordering system, but smart buyers always double-check that CAS number (174899-83-3) before placing an order to dodge any confusion.
Safety & Operational Standards
Handling BzmimCl demands respect in the workplace. Though BzmimCl has a good reputation as less flammable than solvents like ether or acetone, contact with skin or eyes causes irritation, and breathing dust brings health risks. Occupation safety guidelines ask for gloves, protective glasses, and dust masks as normal practice. Older workers saw careless handling of benzyl chloride in the past lead to lasting headaches, so nobody likes to cut corners now. Any area storing this salt needs good airflow to keep vapor and dust to a minimum, and cleanup teams keep spill kits nearby for emergencies. Waste gets labeled as hazardous, and disposal lines up with local authority advice to keep the compound out of landfills and water sources.
Application Area
BzmimCl shows off its skills in more than one arena. Chemists reach for it in the lab when other solvents foul up a reaction. In materials science, workers use it to create or stabilize metal nanoparticles for catalysis or electronics work. Forestry and agricultural companies have tested it for dissolving cellulose—a key step toward making biofuels or upgraded plastics from plants. In pharmaceuticals, it sometimes acts as a greener alternative to old-school, volatile solvents prone to forming hazardous waste. Polymer synthesis and battery technology both benefit from its low vapor pressure and thermal stability, since those traits make for safer, longer-lasting processes and products.
Research & Development
This compound keeps raising eyebrows in research. Every year, new papers show up—some on BzmimCl’s ability to break down tough biomass, others on novel reaction routes made possible by its rapid ion transport. Researchers from universities in Asia, Europe, and America pit BzmimCl against classic catalysts and solvents, sometimes seeing dramatic gains in efficiency or selectivity. Funding agencies now pay special attention to ionic liquids like this one, since green chemistry sits on the priority list for sustainable industrial growth. Every serious R&D lab in green tech or renewable energy marks down imidazolium salts as tools for the future, hoping to nudge ahead of the competition on breakthrough patents.
Toxicity Research
Toxicology teams dig into BzmimCl for a good reason. Compared to older solvents, ionic liquids get a better safety score for volatility, but that doesn’t translate to zero risk. Studies in the past decade looked at aquatic life exposure and found limited but real effects, especially at high concentrations. Chronic exposure in lab animals suggested mild to moderate toxicity, mostly to liver and kidney systems. Modern research tries to balance the clear process improvement BzmimCl brings against these concerns. Farm runoff or dumping after industrial use could become an issue for nearby water sources, so regulators call for rigorous assessment and management. Teams now study alternatives or design BzmimCl analogs to soften these risks in future generations of salts.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, BzmimCl could play an even bigger role in cleaner manufacturing and sustainable chemistry. The world keeps pushing for less waste, safer working conditions, and smaller environmental footprints. Materials that can replace flammable, volatile, or persistent organic solvents without major trade-offs keep gaining ground. As research rolls on, BzmimCl’s flexibility could help build new battery chemistries, unlock efficient biomass conversion, or streamline fine chemical production. The trick lies in testing its limits, controlling toxic by-products, and keeping production costs in check. Better understanding at a molecular level and smarter engineering for lifecycle management mean the story of BzmimCl keeps unfolding—both inside the lab and out in the field.
What Makes 1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride Notable
1-Benzyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride doesn’t show up at the supermarket or land in daily headlines, but it plays a behind-the-scenes role in chemistry labs and research centers. As someone who’s worked hands-on with ionic liquids, I’ve seen how salts like this one open up possibilities for chemists who want to move beyond traditional solvents. With its unique structure, this compound stands out for its ability to dissolve a broad spectrum of organic and inorganic compounds, something classic solvents often can’t manage without a hitch.
Green Chemistry and Safer Solutions
Solvents have a bad reputation, often rightly so. Volatile organic solvents—think acetone or chloroform—create headaches for both health and the environment. 1-Benzyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride belongs to a family of ionic liquids touted as more sustainable. It boils down to safety and efficiency; this salt stays put at room temperature, meaning it doesn’t vaporize so easily and doesn’t fill the air with dangerous fumes. This matters in real-world labs where exposure risks pile up and safety standards can make or break a project.
Catalysis and Synthesis
Chemists crave control, especially during reactions. 1-Benzyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride often steps into the role of reaction medium for organic transformations that hit roadblocks in water or traditional solvents. Take the Suzuki coupling reaction, which connects small molecules to build larger, complex ones. Using this ionic liquid, researchers can boost yields and reduce the number of nasty byproducts. Its ability to stabilize reactive intermediates means that trickier reactions—ones involving sensitive organometallics or polar compounds—unfold with fewer complications.
Extraction and Materials Science
Handling complex mixtures in the lab calls for creativity. In extraction and separation, this ionic liquid helps pull out valuable metals from electronic waste or assists in the isolation of bioactive natural compounds. I remember working through stubborn plant extracts in the lab, only to get higher purities after switching to an ionic liquid-based protocol. Shifting away from harsh acids and bases, labs find damage to equipment and risk to workers drop significantly. The demand for purer pharmaceuticals only intensifies the need for substances like this in separation steps, where selectivity matters most.
Electrochemistry and Beyond
Energy storage and battery research benefits as well. Ionic conductivity stays high and the compound resists decomposition under electric current, making it appealing for battery electrolytes or supercapacitors. Startups focused on green energy look for ways to get reliable charge-discharge cycles without the flammability problems seen with classic electrolyte blends. With its tunable properties, 1-Benzyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride opens doors here too.
Looking Ahead
The bigger conversation surrounds green processes and sustainable materials. Demand for chemicals that pose fewer hazards and offer better recyclability will only climb. Researchers, industry leaders, and regulators keep watching compounds like 1-Benzyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride because its benefits reach into safer working conditions, waste reduction, and smarter resource use. The key is responsible development—limiting toxicity in large-scale production and finding routes to recycle or degrade these salts after use. Choices in the lab set standards across the field, and adopting smarter solvents marks a real move forward.
Chemical Formula and Structure
Talking chemistry can feel a bit daunting, but breaking things down makes it real. 1-Benzyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride is a mouthful name, but its formula, C11H13ClN2, gives a straightforward tally of what’s inside. The molecule includes a benzyl group and a methyl group attached to an imidazolium ring, with chloride as the counterion. Its molecular weight lands at 208.69 g/mol.
Why Knowing Chemical Details Matters
In my work with lab setups, knowing exact formulas often meant the difference between a successful reaction and wasted effort. Laboratories count on precise data, like molecular weight, for tasks such as solution preparation and yield calculation. Taking shortcuts with these details never ends well, especially in pharmaceutical development or high-precision synthesis, where the scale of error can snowball.
Researchers often gravitate toward imidazolium salts like this for their stability and versatility. They play a big part in ionic liquid research. An ionic liquid acts as a solvent, catalyst, or sometimes both, and its unique makeup can open doors that typical solvents just can’t. I remember one graduate project where swapping out traditional organics for an imidazolium-based salt tightened up our process and made separating products a lot easier. Less time with fume hoods and hazardous solvents feels like a win for everyone.
Putting the Properties to Good Use
Applications in green chemistry appeal to students and seasoned chemists alike. 1-Benzyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride often turns up in drug discovery, natural product extraction, and electrochemistry. The salt dissolves a wide range of compounds, including those tough hydrophobics some other solvents ignore. Plenty of innovation flows from this: battery research, bio-catalysis, and polymer science all benefit.
Safety can become a sticking point. Misjudging a material’s toxicity leads to preventable accidents. Many ionic liquids rank lower on volatility than common organics, which helps, but never a free pass—chloride salts, even ones like this, still ask for gloves, goggles, and good ventilation. Reliable sources like the PubChem database show one should avoid direct skin and eye contact. Cleanup routines and clear labeling protect everyone involved.
Solid Research, Real Problems
Access to high-purity chemical salts is not evenly spread worldwide. I’ve seen colleagues rely on inconsistent suppliers, leading to headaches in reproducing experiments. Some countries face import hurdles, with costs far higher than in Western labs. Achieving consistent and genuinely open supply chains can level the playing field, inspiring more young minds to experiment.
Quality control ties closely to the idea of reproducible science. Academic publishers now require authors to describe sourcing and testing in detail. This protects against questionable data, but it also highlights gaps in resource availability. Collaborative efforts—shared funding, open-source supply databases, and regional partnerships—show promise in bridging the gap.
Opening Doors to Greener Chemistry
Chemists worldwide keep pushing boundaries, hunting for solvents and reagents that challenge the old ways. 1-Benzyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride stands out as one tool in this ongoing shift. The story of this chemical, like so many in the field, isn’t wrapped up in a single publication or patent. It sits inside every reaction flask where someone’s bold enough to try something new, test it again, and share their truth with the next curious mind. Reliable formulas and accurate weights help those stories keep rolling.
Digging into the Chemistry
Solubility stands as one of those plain but powerful facts in chemistry. A compound either dissolves in water or doesn’t. Take 1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride. On paper, it carries a hefty name and a reputation among ionic liquids researchers. The burning question, though, is simple: do you get a clear solution when you mix it with water, or do you end up with clumps at the bottom of the beaker?
This compound falls into the class of imidazolium salts. They often show up in labs investigating greener solvents. The structure plays a big part here; the chloride anion pairs up with the large, ionic imidazolium cation. From experience in the lab, a compound’s ability to mix with water doesn't just depend on its charge. The size of the ion and how it fits into the water structure matter, too. Imidazolium-based salts with smaller alkyl groups, like 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride, mix well. If you swap out an ethyl for something bulkier, water often accepts the new guest, but not always as warmly.
What Happens in Water?
Scientists have run these experiments time after time. The word from literature and actual benchwork: 1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride dissolves in water. This makes sense considering both the chloride ion’s love for water and the charge carried by the imidazolium ring. Still, that benzyl side group gives a nudge towards lower solubility compared to smaller siblings in the same chemical family. Yet, you won’t find leftover crystals floating around in a standard lab mix. Water handles the job.
Why Should This Matter?
A simple “yes” to solubility isn’t newsworthy by itself. The real story begins with how this fact gets used. Labs and industries looking for greener solvents care about compounds like this. Imidazolium salts, including 1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride, show up in battery research, chemical synthesis, and even materials recycling. Water solubility keeps handling safer and opens doors for waste treatment. Try disposing of an oily, insoluble salt and headaches soon follow. Mix in water-soluble ionic liquids and the environmental impact shrinks.
It also affects the chemistry downstream. Soluble salts provide flexible reaction environments—chemists can control ion concentrations and run cleanup steps more smoothly. Solubility makes recovery easier. Push hard on separation and purification, costs jump, and green credentials fade.
Balancing Benefits and Drawbacks
The game never stops at “does it dissolve?” It’s about what happens next. Solubility sometimes means easier handling but can also hint at higher aquatic toxicity if waste escapes into rivers or lakes. Regulatory frameworks already flag ionic liquids for careful study. My own work with these salts has driven home the need for clear protocols. Use closed systems, employ high-grade filtration, and track waste streams so research progress doesn’t come at the environment’s expense.
Paths Forward
Solubility data only earn their keep if put to work responsibly. Detailed studies like those led by IUPAC panels provide clear guidelines. In academic circles and industry labs alike, sharing both the data and the best practices aids everyone. The future of ionic liquids, including 1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride, depends on matching chemical curiosity with practical safety. Every lab run blends science with stewardship, especially when water-soluble salts step onto the stage.
Understanding the Substance
1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride comes up in quite a few labs, especially for folks working with ionic liquids or catalysts. If you’ve opened up a jar of it or even handled a small vial, you already know that it clumps up fast and pulls in water from the air. That behavior has real consequences, both for the shelf life and for anyone who expects reliable results from their research or production process. Chemical stability isn’t just a technical detail—it drives accuracy and keeps people safe.
The Risk of Moisture
This chloride salt loves moisture. Leave it out on the bench for a day or two and you’ll notice a big difference in texture and even color, especially if you live in a place that’s humid. Water can get into the lattice of this compound and start to break it down or even alter its chemical properties. At that point, what you have in the bottle is no longer what you bought or synthesized. Anyone who has had to re-run an experiment because their material became “off”—not to mention risking ruined batches—knows the headache that brings. If you’ve got a few grams of it, think about what happens to a kilo sitting neglected on a shelf.
Safe Storage Practices
When I worked in a university lab, someone once left a sample of 1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride in a zip-lock bag, sitting out over a long weekend. It took on water, got lumpy, and nobody could get it to dissolve the way it had before. The lesson there: air-tight containers matter. Glass jars with screw tops or PTFE-lined caps do the job; add a bit of silica gel in the container if you can. Some people wrap their containers with a layer of parafilm as extra insurance. These aren’t complicated moves, but they save real money and time down the line.
Set the storage area apart from sinks or busy separators to limit accidental exposure to humidity. If your lab or workspace swings in temperature, the risk only grows. Large swings make condensation within the container more likely, which introduces yet more water. That’s a hidden risk that’s easy to overlook until it's too late. Keeping things in a controlled environment—think dry, cool, out of direct sunlight—pays dividends. In my experience, a dedicated desiccator does wonders. Even a simple, tight-sealing cabinet beats a cluttered open shelf near the hot plate.
Labeling Goes a Long Way
Too many containers end up with half-peeled labels or cryptic marker notes. If someone accidentally stores this chloride in the wrong place, or if a new researcher doesn’t know which compound breaks down quickly, mistakes happen. Take the time to write clear labels with dates, full names, and concentration or batch info. This habit prevents confusion down the line. I’ve seen labs where missing labels caused unplanned expenses and dangerous mix-ups; these are easy problems to avoid.
Personal Protective Equipment and Spill Response
This compound isn’t especially hazardous compared to some others, but basic precautions go a long way. Keep gloves handy and wear a lab coat. If anyone spills, use dry paper towels and avoid water, since water makes some of the mess trickier to clean and contaminates other chemicals. Dispose of contaminated materials according to local waste rules, and check the safety sheet if there’s any doubt.
Solving Storage Issues Together
Train everyone who handles chemicals, not just the grad students or chemists. Make it routine to check storage conditions, rotate stock, and toss anything showing signs of clumping or degradation. Regular audits build accountability. An organized, well-labeled shelf and climate control stand as simple moves that protect people and budgets, with no expensive tech required.
A Closer Look at 1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride in the Lab
Most people who spend time in a lab or handle specialty chemicals have come across names like 1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride. This compound finds its way into everything from advanced organic synthesis research to green chemistry projects. Curiosity aside, handling it safely isn’t optional. Exposure or spillage usually turns into a headache for everyone involved, and with strict regulations in place, there’s simply no excuse for carelessness.
Real Stakes with Personal Protection
Experience has shown me that most mishaps come down to skipping basics. It’s all too easy to assume gloves and goggles do the trick. For this compound, latex or nitrile gloves block most risk of skin contact, but the protection doesn’t stop there. Splash goggles shield the eyes, and a lab coat or apron keeps the chemical from contacting street clothes or skin. Over the years, I’ve seen small spills eat holes through cheap gloves and cause quick skin irritation—the kind you notice fast and regret even quicker. Nobody benefits from shortcuts.
Ventilation and Air Quality Matter
Working with imidazolium salts in a lab without a decent fume hood is asking for trouble. Some folks figure if it doesn't smell sharp or turn cloudy, the vapors aren’t a problem. That’s just false confidence kicking in. Good engineering controls, like local exhaust systems or chemical fume hoods, keep the workspace safe. I’ve learned to check airflow before uncapping anything, even if I’m just weighing out powders. Airborne dust can linger and expose the next person, not just the person handling it first.
Spill Response Isn’t Fancy, Just Practical
Spills happen to the best, whether you’re new or have spent decades at the bench. The smart move is having an easy-to-access chemical spill kit on hand. I’ve cleaned up minor dry powder spills by scooping with a spatula and damp towel—never dry sweeping, since that just whips up more dust. Used towels and all contaminated waste belong in a labeled, sealed bag until disposal. Housekeeping in a lab is never about neatness—it’s about not letting risks multiply for the next user.
Storage: Simple Steps That Make a Difference
Storing chemicals properly used to feel like an afterthought. It only took a couple of ruined batches and one ruined shelf to teach me otherwise. This chloride compound hangs onto moisture, so a tight-sealed container away from direct heat or sunlight keeps it in its best condition while reducing accident risk. Avoid stacking with acids, oxidizers, or anything reactive. All containers need real labels and must sit on a designated chemical shelf—not stuffed under a sink or with household cleaning supplies.
Training: The Most Reliable Safety Tool
Every person, from students to professionals, really learns safety best from hands-on experience. Written protocols rarely have impact unless someone demonstrates them face-to-face. At my old lab, new students ran through a safety quiz before touching a thing, followed by a walk-through of the MSDS for every reagent. Talking through hazards and reviewing real incident stories hit home in a way printed warnings never did.
Why It All Matters
Serious accidents rarely stem from ignorance. Most come from overconfidence or rushing for results. Safety culture takes a mix of practical tools, honest sharing of experience, and clear procedures anyone can follow. 1-Benzyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride deserves respect for what it can do—both scientifically and in terms of risk. Solutions come from a real sense of accountability, not fear.