1-Hexyl-3-Methylimidazolium Methanesulfonate: An In-Depth Look
Historical Development
Curiosity fuels progress. As chemists searched for alternatives to volatile organic solvents, they started tinkering with ionic liquids. In the 1990s, a string of imidazolium compounds earned new attention because they held promise as safer, more tunable media for challenging chemical work. 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazolium methanesulfonate (often called [HMIM][MeSO3]) grew out of this wave of experimentation. With governments and industry pressed to cut environmental hazards, minds turned toward salts that act as room-temperature liquids. The industry adopted these materials slowly, but the steady drive for cleaner, more efficient processes made room for compounds like this one on production lines and in research labs.
Product Overview
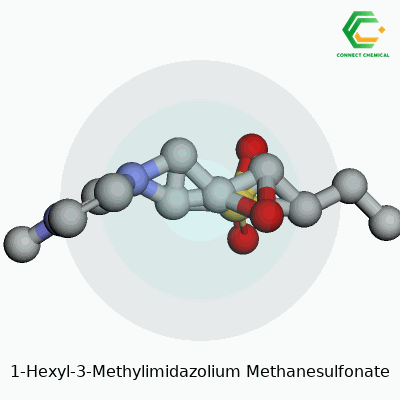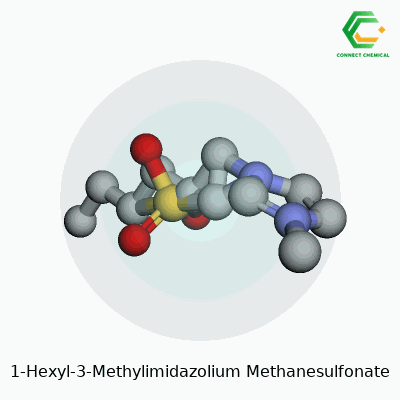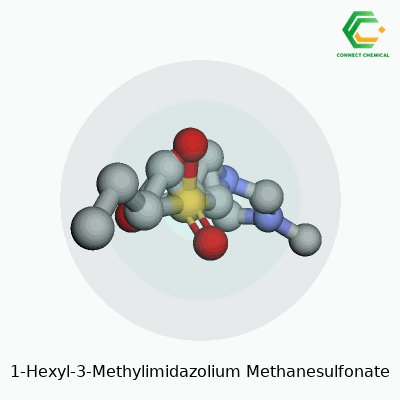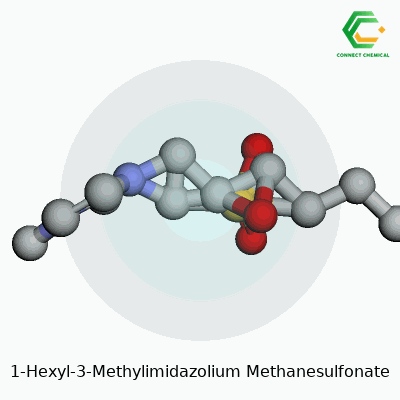
1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazolium methanesulfonate stands out as an ionic liquid with remarkable solvation abilities. It holds together as clear, slightly viscous liquid at room temperature. The imidazolium core allows for strong ionic character; the methanesulfonate anion brings in stability and low volatility. This liquid offers strong resistance to air and some organic solvents. With negligible vapor pressure and a broad electrochemical window, chemists value its flexibility and safety compared to solvents like chloroform or acetonitrile.
Physical & Chemical Properties
This compound comes as a colorless to pale yellow liquid, with a faint odor. Its molecular formula, C11H22N2O3S, hints at its robustness. The density stays close to 1.14 g/cm³ at room temperature. It can manage temperatures above 200°C before decomposition starts. The ionic nature gives it high viscosity, usually settling near 100–500 mPa•s at 25°C. It mixes well with water, alcohols, and certain polar organics. The melting point drops below standard room temperature, supporting its place in the “room-temperature ionic liquids” group. Chemically, it resists oxidation and hydrolysis under mild conditions. The wide liquid range allows scientists to run demanding reactions in it, whether for synthesis or separations.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Producers typically mark it with purity grades exceeding 98%. Labels must name the full chemical title—1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazolium methanesulfonate—alongside common abbreviations like HMIM-MS or [HMIM][MeSO3]. Containers often bear batch numbers and safety codes under the GHS and REACH standards. Product sheets cover data about physical state, pH (usually slightly acidic), water content, and electrolyte properties. Correct labeling isn’t just paperwork; it builds trust for scientists who need reproducible results, and it avoids cross-contamination on the bench.
Preparation Method
Typical synthesis follows a pair of straightforward steps. It starts with creating 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium halide by reacting 1-methylimidazole with 1-chlorohexane. Then, chemists use metathesis: they mix the resulting halide with sodium methanesulfonate in water, and the product separates out. Careful washing removes salts and unreacted precursors. Drying under reduced pressure or in a desiccator clears away traces of moisture. Batch records track yields and waste, which supports both quality and regulatory needs. The process avoids aggressive reagents, which keeps workers safer and environmental liability lower.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
This ionic liquid plays a double role. On one side, it acts as a solvent for tough organic and inorganic syntheses. On the other, it joins chemical reactions through ion exchange, stabilization, and phase transfer. People have grafted various functional groups onto the imidazolium ring to tailor hydrophobicity or tweak solubility. In electrochemistry, [HMIM][MeSO3] helps shuttle ions and boosts electrodeposition selectivity. Mix it with transition metal complexes, and it sometimes changes catalytic activity or solubility. Modifications focus on strengthening its thermal stability or stretching the electrochemical window for next-generation batteries and supercapacitors.
Synonyms & Product Names
This compound moves through the chemical world under several names. Synonyms include 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium mesylate, HMIM-MS, [HMIM][MeSO3], and 1-Hexyl-3-methylimidazolium methylsulfonate. Catalogs occasionally mix up “methanesulfonate” and “mesylate.” For research and commerce, the CAS number (usually 740617-36-1), structures, and detailed chemical names help avoid confusion.
Safety & Operational Standards
Everyone handling [HMIM][MeSO3] needs good protective habits. Though less hazardous than most volatile solvents, it can irritate skin and eyes with prolonged contact. Spills don’t produce clouds of dangerous vapor, but the liquid will seep and stick, so labs keep plenty of absorbent and proper PPE at hand. Long-term inhalation or swallowing tests haven’t raised major alarms, but it makes sense to work with exhaust fans and avoid direct skin exposure. Disposal runs best through incineration, given the salt-like nature. Major chemical safety sheets, including OSHA and ECHA guidelines, recommend full gloves, goggles, and splash-resistant coats during routine use. Adoption of closed systems and regular safety training stops lab mistakes from becoming accidents.
Application Area
This ionic liquid lights up modern laboratories, especially where researchers want to skip flammable or toxic traditional solvents. [HMIM][MeSO3] runs as reaction media for organic synthesis, where it smooths out difficult steps, like alkylations or cyclizations, that choke with regular solvents. People use it for extraction processes, pulling valuable metals from ores, or separating rare earths. Electrochemical cells rely on its wide liquid window and inertness—it pops up in advanced batteries and fuel cells, including some used for energy storage prototypes. In biochemistry, scientists test it for enzyme stabilization and biotransformations, aiming for greener routes to drugs and flavors. Its anti-microbial action even shows up in polymer production. Industrial firms turn to ionic liquids like this to improve process yields and reduce fugitive emissions, inching closer toward sustainable chemistry.
Research & Development
Published studies focus on the rich interplay between structure and function within this family of liquids. Many labs probe how minor shifts in the hexyl chain or ring substitutions affect melting points and solubilities. Electrochemists keep testing it for new battery designs, chasing longer lifespans and less chance of fire. Catalysis research leans on its ability to change reaction rates and outcomes, especially when linked to precious metal ions. Others look for ways to use it as both solvent and reagent, slashing the number of chemicals needed for a process. The drive to replace toxic organics in everything from pharmaceutical syntheses to plastics pushes researchers to develop cheaper, scalable ways to make ionic liquids and recycle them reliably.
Toxicity Research
So far, long-term studies suggest that [HMIM][MeSO3] avoids many of the usual pitfalls of volatile organics. Acute toxicity for mammals stays low, according to rat and mouse studies. High doses prompt gastrointestinal distress and mild liver markers, but fatal doses lie well above levels used in practical settings. Chronic exposure research has started uncovering mild eco-toxicity, mainly tied to aquatic species—probably from disruption of cell membranes. Compared to older chloride-based imidazolium salts, the methanesulfonate variant causes fewer persistent bioaccumulation issues, as it breaks down faster and resists lingering in the environment. Bioassays, fish embryo tests, and degradability trials form a growing pool of data, all aiming to inform smarter risk management.
Future Prospects
Researchers keep pressing for even greener, smarter ionic liquids, and each study on [HMIM][MeSO3] opens new doors. Big breakthroughs may come from coupling this chemistry with biotechnology or advanced materials science. Future batteries—running safer, longer, with better recyclability—might rely on tweaks to this family of compounds. In industry, demand for sustainable solvents will only climb as rules tighten and the cost of pollution rises. Expect more automation around its production and purification, along with software-driven screening to predict its behavior in new reactions. Work on toxicity and bio-breakdown keeps a watchful eye on both human health and environmental impact, supporting both innovation and stricter standards. With the chemists’ appetite for safer, cleaner, and smarter solutions, 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium methanesulfonate looks set to stay central to the next generation of clean chemistry tools.
The Rise of Ionic Liquids in Real-World Labs
Years ago, I worked in a research lab that kept bottles lined up according to their function. Solvents sat on one shelf, strong bases and acids on another. One day, our team received a sample of 1-Hexyl-3-Methylimidazolium Methanesulfonate. At first, we raised eyebrows. The name alone sounded impressive—and a bit intimidating. Yet, this ionic liquid soon showed that it wasn't just another chemical oddity, but a workhorse in the hands of scientists and engineers.
Green Chemistry Gets a Boost
This compound, with its bulky imidazolium core and long hexyl side chain, doesn’t evaporate easily. This means it won’t float off and get into the air we breathe, which gives it a leg up over classic solvents like chloroform or benzene. Sustainability in the chemical industry needs real shifts, and swapping volatile solvents for ionic alternatives like this one marks a step forward. Toxicity profiles tend to rate lower than older, traditional solvents, and that often means safer working conditions in the lab and factory.
Catalysis and Organic Synthesis
I’ve watched colleagues in organic chemistry swear by ionic liquids for tricky reactions. Some catalysts struggle in water or regular organic solvents, but the unique properties of 1-Hexyl-3-Methylimidazolium Methanesulfonate let reactions run more smoothly and sometimes even with better yields. Recyclability stands out—after the reaction, this ionic liquid often gets filtered out and re-used. For labs watching their budgets or aiming to shrink their waste, that's a big deal. Published studies report this salt helping in alkylation, Diels-Alder, and even some pharmaceutical syntheses.
Electrochemistry and Batteries
Ionic liquids have found a solid home in electrochemical devices. In my time talking with engineers designing new types of batteries and supercapacitors, 1-Hexyl-3-Methylimidazolium Methanesulfonate pops up in discussions about electrolytes. Its low flammability and thermal stability cut down fire risks compared to older battery solvents. Electric vehicles and grid-scale storage are hungry for new materials, and this ionic liquid shows up in experiments aiming to push the boundaries of safe, long-lasting devices.
Extraction and Separation Technology
Environmental cleanup calls for smart solutions—especially when dealing with heavy metals or organic toxins in water. This ionic liquid grabs certain metals out of solutions, making it useful for treating wastewater from mining, industry, or even electronic waste recycling. Selective extraction means less waste generated on the back end, which matters for companies trying to keep costs down and comply with tough rules on pollution.
Challenges and The Road Forward
No chemical fixes every problem. 1-Hexyl-3-Methylimidazolium Methanesulfonate, for its strengths, carries challenges. Sourcing and manufacturing can push up prices, so industries have to weigh the green benefits against their budgets. Some early studies point out environmental persistence. Responsible disposal matters, and researchers are working on both breaking down spent liquids and inventing salt structures that degrade more easily after use.
Innovation Over Hype
From first-hand experience in labs and through talking to builders of clean-tech startups, I’ve seen the drive to turn promising chemicals into real solutions. 1-Hexyl-3-Methylimidazolium Methanesulfonate stands out not for splashy headlines, but for its steady utility across synthesis, extraction, and electrochemical tech. Experts keep studying its impact, risks, and scope. With care, better regulation, and open info-sharing, its positive impact can spread further—one breakthrough at a time.
The Real Story in the Details
People talk about purity in products like it’s just a number, a percent on a certificate. In labs and factories, that number decides the next steps, shapes costs, and affects safety. I remember reviewing a batch of raw material for a medical device—noticing a slight tint, a little haze that shouldn’t have been there. That moment made it clear how small details can signal big problems. Even tiny impurities bring big risks, whether you’re mixing painkillers or chemicals for food packaging.
What Purity Looks Like in Practice
A pure chemical stands out—you notice the clarity, a glassy or powdery finish with nothing floating or clumped together. A food ingredient with high purity won’t carry mystery flavors or grit that makes chefs question if a product deserves shelf space. I once tested salt for a packaging company. Pure salt pours freely. It looks bright, almost luminescent under bright light. You spot fake blends because there’s dust, hard chunks, or even strange off-white spots. People who ignore these signs end up with equipment that clogs up or food that spoils days earlier than it should.
Pharmaceutical labs take things even further. White doesn’t just mean clean—it means no hints of yellow, no beige shading, no remnants of chemical processes that finished hours before. If pills show tiny specks or different colors, quality control stops production. I’ve seen a whole week’s work tossed out over a single batch of discolored powder, just to avoid questions about patient safety down the line.
Why Purity Impacts Confidence
Trust rides on more than just printed lab results. People want to believe in what they use and eat. If a vitamin powder opens up and looks gray and clumpy, customers can tell something’s off even before tests come back. No one wants to gamble with their family’s health or their company’s reputation. Most buyers these days ask for certificates and pictures, but they also rely on their own eyes. They break seals, pour samples out, sniff, even taste. Selling something that looks questionable destroys future business. Nobody forgets a foul-smelling powder or a liquid that stains beakers.
Getting Purity Right, Every Time
Good practice doesn’t happen by accident. Producers focus on clean source material, careful storage, and simple but tight packaging. Clear labels and batch records keep things honest. It’s easy to say numbers prove purity, but nothing replaces basic tests: does it dissolve as it should, does it behave under the microscope, does a trained technician say it matches last month’s lot? When things don’t look right, it helps to stop everything and fix the issue long before it reaches another pair of hands.
People in the supply chain—producers, scientists, warehouse staff—need steady training. Everyone has to recognize what purity means in their field. One mistake can ripple out through food mixes, pills, glues, paints. A culture that values careful inspection and quick communication cuts down on surprises. Purity and appearance aren’t just technical hurdles; they’re the foundation of trust that no company can afford to lose.
Paying Attention to Everyday Lab Safety
I remember the first time I saw a bottle labeled “1-Hexyl-3-Methylimidazolium Methanesulfonate” on a shelf in the back of the lab. To someone new, the name looks intimidating, but smart handling of any specialty chemical starts with the basics: storing it in the right conditions, labeling it clearly, and checking its shelf every so often. You don’t need decades of experience to realize harsh lighting, open containers, or cluttered refrigeration risks don’t belong in a space where you keep ionic liquids.
Temperature and Climate Matter
This compound, found in many labs for its ionic liquid properties, holds up best at room temperature, tucked away from moisture and heat. Labs with spotty air conditioning or high humidity often see bottles go bad earlier than they should. A dry cabinet away from sunlight helps, but not all cabinets are created equal. Some places try to save money and use makeshift shelving near vents or sunny windows—this kind of shortcut always backfires. Keeping it dry and cool guards against hydrolysis and other surprise changes in appearance or function.
Protecting from Water and Air
Moisture likes to sneak in wherever it can. I’ve seen more than one scientist pour a bit from a container, cap it loosely, then set it back without a second thought. Water vapor in the room can find its way in after just one rushed afternoon. In my own routine, I double-check that the lid is tight and the cap shows no signs of “sweating.” If you leave it unsealed or let it sit out, the integrity slips fast, putting research at risk and costing more in replacements and wasted effort.
Clear Labeling Earns Its Keep
Nothing sours a workday like reaching for a bottle and realizing the label peeled off months ago or faded under harsh lights. Scrawled handwriting or blurred ink only add to confusion. I’ve avoided enough accidents by making sure every container shows the chemical name, date received, and the initials of the person who opened it. Quick checks prevent old stock from mixing with new and cut down on the chance of using sensitive materials that have already lost their punch.
Ventilation and Spill Prevention
Kitchens have their rules, and chemistry spaces do too. Strong-smelling compounds or those with low volatility still deserve a bench with decent airflow. I like to keep all liquid storage away from the edge of a countertop to avoid knock-overs. Securable trays underneath containers add a second line of defense against drips. I’ve seen the damage a slow leak can cause, not just to experiments, but to the benches and the people working there. Quick attention to leaks spares everyone headaches and keeps the workspace safer.
Training and Routine Checks
Every time a new group of students or interns rolls through, I lay out the basics: Keep bottles sealed, date everything, and clear away old materials even if you’re not the one who opened them. Simple habits keep bigger problems from building. I recall a project that dragged on because someone ignored a “dispose by” date, which led to contamination. If everyone approaches these tasks with the same care they use outside the lab—checking milk before pouring, screwing a cap on a jar—you can cut out most headaches tied to chemical storage.
Everyday Chemicals, Everyday Risks
People cross paths with all sorts of chemicals daily. Soap on the bathroom sink, cleaning sprays under the kitchen counter, even that garden fertilizer in the backyard—each one made up of compounds serving a job. Safe on the shelf doesn't mean safe in every circumstance, though. Something as simple as bleach, for example, works wonders on stained laundry, but nobody wants to breathe it in or let kids near it. Laxity in handling these everyday products often lands folks in the emergency room.
Real-Life Lessons From Work and Home
I've learned details about chemical safety the hard way, both in my time working construction jobs and through accidents at home. On a site, I saw what happens when paint thinners mix with poor ventilation—headaches, wheezing, lost work hours. At home, a slip-up with drain cleaner sent my cousin to urgent care. Both moments drove the same point home: product labels, with all their fine print, really mean business.
How to Get the Facts
Instead of guessing, good information makes the difference. Products come with material safety data sheets, often called SDS. These documents run through hazards—eye burns, flammable vapors, or nasty reactions. An SDS doesn't just tick some compliance box. I’ve leaned on those sheets while training new hires or picking out replacements for dangerous solvents. Reliable guidance from those sheets saved my crew from more than a few hospital trips.
For household goods, labels tell a similar story. Manufacturers don’t print "use in a well-ventilated area" for fun. Following those directions keeps families safe. Keeping heavy-duty chemicals on the bottom shelf with a childproof latch seems small, but it beats spending a night in the ER.
Facts Behind the Danger
Some compounds harm at even tiny doses. Mercury, lead, and asbestos still show up in older buildings and cause lifelong problems after brief exposures. Breathing silica dust, often present in construction work, brings a risk of lung disease. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report thousands come down with chemical-related illness each year, from industry pros to home DIYers.
Risks show up fast during accidents, but long-term exposure matters just as much. Backyard pesticides or hobby shop solvents can build up in the body and lead to health troubles years down the line. I’ve seen more than a few retirees with respiratory problems, many because safety gear sat unused for too long.
Building Smarter Habits
Safety starts with respect. Wearing gloves, goggles, or a mask, even for small jobs, feels tedious until you picture the consequences. I once scoffed at respirators—until I developed a cough that stuck around long past a kitchen remodel. Ventilation is another overlooked detail. Leaving windows cracked and running fans pushes dangers outside before they land in your lungs.
Storing chemicals away from food and out of reach for kids or pets seems easy. But it’s the corners people cut—just for “one minute”—that turn into emergencies. I’ve had to learn the value of patience and preparation; skipping a step has never saved real time in the end.
Moving Forward with Common Sense
Staying safe around potentially hazardous compounds doesn’t mean steering clear of every cleaner, spray, or polish. With a little common sense—reading directions, gearing up, and paying attention—risks drop fast. Anyone handling chemicals, at home or on the job, holds the key to their own safety. The more people share experiences and tips, the easier it gets for everyone to avoid learning these lessons the hard way.
The Real-World Value of Identifying Chemicals
CAS numbers stand out as a stamp of clarity in a chemistry world packed full of confusion. Every substance gets its own number, not unlike a social security number. This unique tool helps chemists stop guessing and get down to precision. At work, nobody wants to order the wrong solvent and deal with hours of cleanup or wasted resources. That kind of mistake can run up costs and close off opportunities for progress.
How Overlapping Names Lead to Confusion
Lots of chemical names trip people up. A common solvent like acetone might show up as “propanone,” “dimethyl ketone,” or good old “nail polish remover.” Too many names open the door to mistakes, especially when the safety on the line. The CAS number cuts right through the problem. It gives researchers, suppliers, and even emergency responders the fast way to check what's really in that bottle or shipment.
The Weight of Trust in the Lab and Industry
Years back, I saw a coworker grab a bottle for our analysis only to realize halfway through the experiment that it contained a nearly identical chemical with a different effect. That tiny mistake forced us to repeat eight hours of work and adjust all our data. Once we adopted CAS numbers as a routine checkpoint, mixups dropped to almost zero. Chemical suppliers rely on these numbers too, particularly for hazardous materials where getting the right match can mean the difference between routine process and accident report.
The Molecular Formula: Not Just for Theory
Knowing the molecular formula isn’t just for passing chemistry class. Say you’re in pharmaceuticals, and the molecular formula lets you calculate exact dosages, avoid dangerous side reactions, or spot if an impurity sneaked in. Even simple household products depend on precise formulas to guarantee performance and safety. Looking at databases or regulatory files, missing the molecular formula will hold up approvals and trigger endless back-and-forth with government agencies.
The Role of Data Integrity and Modern Tech
Trustworthy data forms the backbone of real progress. Tools like SciFinder and ChemSpider pull from millions of compounds, and they use the CAS registry as a key reference. Regulators and researchers worldwide rely on these details, which means mistakes or poor recordkeeping don’t just slow things down—they can wreck reputations and affect public health. The molecular formula steps in as critical evidence: it describes the substance’s core composition at a glance, exposing errors before they turn costly.
Building Better Solutions for Reliable Chemistry
Companies should push for better integration between their purchasing software and public chemical databases. Scanning barcodes linked to CAS numbers can help track stock and avoid costly duplicate orders or expired materials. Training staff to double-check formulas alongside product codes keeps labs safer and more productive. Regulatory bodies could go further to require digital records of CAS numbers with shipping papers or import documentation.
Consumers might not think about CAS numbers at the store, but this system underpins the reliable, tested products stacked on every shelf. Sticking with trusted identifiers keeps creativity flowing without sacrificing transparency, safety, or trust.