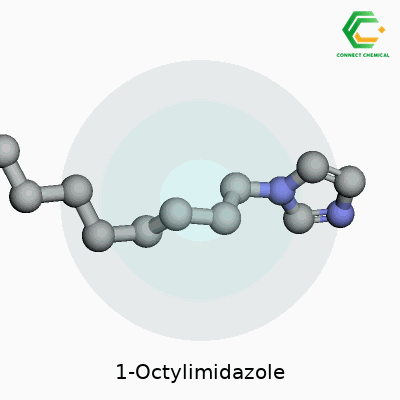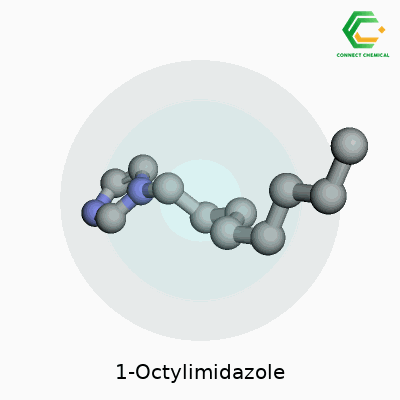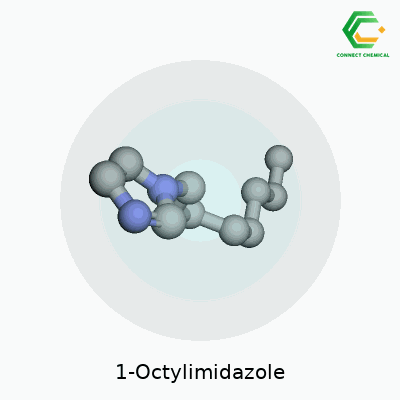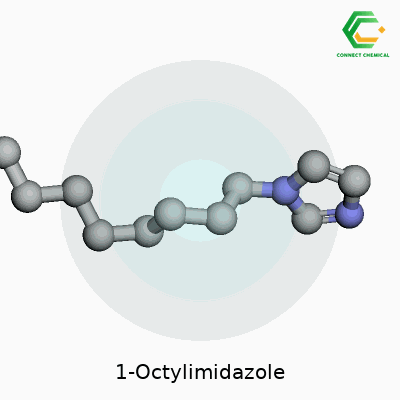
1-Octylimidazole: Breaking Down a Modern Chemical Workhorse
Historical Development
Chemists started looking at imidazole compounds shortly after the turn of the twentieth century, hunting for building blocks that could fuel a rise in novel materials and bioactive molecules. Before long, someone figured out that tagging imidazole—an aromatic heterocycle with punchy properties—with an octyl side chain gave it a whole new set of uses. Synthesis took patience, often stretching out over days using early organic methods. Once researchers got good at making 1-octylimidazole reliably, they found it bridged a gap between the water-loving imidazoles and long-alkyl-chain molecules that preferred oils and solvents. Historical patents from the 1960s and '70s started recording its role in the surge of ionic liquids, surfactants, and functional coatings, making it a quietly essential chemical in the background of industry. I came across its surging popularity while scanning through decades of chemical abstracts in the lab, and it surprised me how many patents still cite early Russian and German synthetic work.
Product Overview
1-Octylimidazole usually comes as a clear, sometimes faintly yellow, liquid. With the octyl chain hanging off the core, this molecule stays fluid at room temperature but avoids the volatility and harsh smell of shorter alkyl imidazoles. People working in labs value its balance—a molecule that dissolves ironically well in both polar and nonpolar solvents, able to merge with a range of reaction mixtures. It forms a backbone for a suite of other imidazole-based chemicals, gives hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces a handshake, and activates tricky transformations in organic synthesis. Commercial product catalogs often list it under specialty chemicals, lab reagents, and customized intermediates, but it rarely gets the attention of flashier chemical names. I remember seeing it on chemical supply shelves, labeled plainly but regularly replaced.
Physical & Chemical Properties
This compound, with the formula C11H20N2, weighs in at about 180.3 g/mol. Its melting point stays well below freezing—usually around -20°C—while the boiling point creeps up past 300°C. In practical lab settings, it refuses to dissolve completely in water, thanks to the octyl tail, yet still offers excellent solubility in ethanol, dichloromethane, and most organic solvents. Unlike shorter alkyl imidazoles, 1-octylimidazole tends not to irritate my nose during handling, and it resists the evaporative loss that plagues lighter analogues. Its structure, with a hydrophobic tail and charged ring, makes it susceptible to strong acids and bases but stable toward most oxidants, a trait that sees widespread use for both preparative and industrial chemistry.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Most suppliers offer 1-octylimidazole at purities above 98%. Documentation usually lists it alongside its CAS number—20549-72-4—and warns about storage below 30°C, out of direct light. Labels highlight the need for gloves, goggles, and a functioning fume hood. SDS sheets stress its low acute toxicity but advise caution over skin and eye contact, as with practically all organic amines. Suppliers roll out quality-control specs like GC purity, max water content, and precise molecular weight checks, so every batch matches what’s on the label—something that used to trip up researchers back in the 1970s during synthesis scale-up. Batch-to-batch consistency still matters for applications in ionic liquids and catalysis where even trace impurities throw off results.
Preparation Method
Synthesis often runs through an alkylation route. Laboratories pair 1-bromooctane or 1-chlorooctane with imidazole, usually under heat in basic conditions. Solvents like DMF or toluene turn out reliable yields, though some scale-up processes lean on phase-transfer catalysis to keep mixing and cost in check. Purification runs through vacuum distillation or column chromatography, trimming away unreacted starting material and off-byproducts. I used to watch this process in the lab, and small shifts in temperature or pH made the difference between a clean product and oily residue. Commercial production tweaks these steps to churn out kilos at a time, banking on efficiency and tighter waste management.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
1-Octylimidazole stands out for the way it accepts further modification at its imidazole ring and the flexible octyl chain. It acts as a nucleophile in alkylation, acylation, and sulfonation, making it a crucial intermediate for ionic liquid synthesis, functional surfactants, or as a precursor for catalysts. Its nitrogen atoms make it reactive toward electrophiles, and the ring tolerates moderate ring substitutions for customized reactivity. Researchers in my group leaned on its reliability for tweaking solubility and phase behavior when developing new materials during grad school. One chemist even used it to tailor enzyme-mimetic environments, taking advantage of its predictable chemical personality and compatibility with both organic and aqueous phases.
Synonyms & Product Names
Across catalogs, you'll spot 1-octylimidazole listed under a handful of synonyms: N-octylimidazole, 1-octyl-1H-imidazole, and imidazole, 1-octyl-. Suppliers sometimes tuck it into larger chemical lines of N-alkylimidazoles, and researchers jot it down as C8-imidazole or simply "octyl imidazole" in notebooks. Having a set of reliable names clears up confusion, particularly in multi-language literature searches, and avoids costly mistakes in chemical procurement.
Safety & Operational Standards
While 1-octylimidazole ranks lower on hazard lists compared to caustic reagents, labs never treat it lightly. In my own lab work, standard operating procedure meant full gloves, goggles, and ventilation—especially during purification, because splashes still irritate eyes and skin. SDS entries list mild acute toxicity, mostly irritation risks rather than systemic damage, but spill protocols remain firm. Facilities usually keep it in tight-capped bottles behind chemical-resistant doors, scanning for leaks or odors. Waste disposal involves neutralization, then passing through solvent waste management programs, a detail driven home by university safety audits.
Application Area
1-Octylimidazole got its break with the rise of ionic liquids, where it serves as a cation precursor for salts with tailored melting points and conductivities. Chemical manufacturers pour it into catalysis, lubricants, and as an intermediate for specialty surfactants. In research, it acts as a phase-transfer agent or as a ligand in coordination chemistry, bridging metals and organic phases. The pharmaceutical sector sometimes uses its derivatives as solubilizing agents or as part of chemical libraries in drug discovery. Materials science engineers look to it for creating anti-corrosion coatings and stabilization agents in resins—my own foray into using it came during a project developing anti-static coatings for electronics, where its structure kept the coating flexible and durable under heat.
Research & Development
Academic teams keep returning to imidazole derivatives, and 1-octylimidazole features in research papers that span from new organic conductors to improved enzyme mimics. Researchers have tested its use in ionic liquids that dissolve cellulose, a game-changer for biomass processing and renewable fuels. In recent years, Green Chemistry groups have tried biocatalytic methods for its synthesis or aimed at recycling routes, both aiming to cut down on energy and solvent use. I once worked on a project leveraging its ionic liquids for deep eutectic solvent design, and we found its precise balance of hydrophobic and hydrophilic tendencies allowed for custom solvent systems with a lower carbon footprint than traditional petrochemical options. Ongoing research explores embedding it in polymers, tweaking electronics behavior for next-gen flexible circuitry.
Toxicity Research
For years, toxicologists found that long-alkyl imidazoles have fairly low acute toxicity in animal models. Most risks come from skin and airway irritation—direct exposure usually causes redness or mild inflammation, but doses high enough to cross systemic toxicity lines require large, unrealistic exposures. Still, the chemical’s impact on aquatic life draws more attention. Studies show that unmodified release can cause bioaccumulation in water systems. Regulatory risk assessments flagged its moderate aquatic toxicity, pushing for careful containment in industrial applications. Long-term chronic effects have not fully unfolded yet, and regulatory agencies remain cautious, especially as ionic liquid use expands. Lab safety offices all but insist on proper gloves, eyewash stations, and prompt response to spills, a routine that reflects the compound’s tricky balance between useful and potentially problematic.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, 1-octylimidazole stands ready to play a role in the shift to greener chemistry, particularly if manufacturers scale up cleaner synthesis and recycling options. Its utility in materials design and catalysis stays strong, as industries hunt for functional chemicals that can slot into low-waste, low-energy processes. With continued research into its environmental fate and chronic effects, safer use guidelines will evolve, supporting a broader reach across specialty and commodity sectors. As flexible electronics, green solvents, and next-gen pharmaceuticals expand, this molecule could shed some of its unsung status and anchor new advances in sustainable manufacturing. Chemists, engineers, and safety professionals will need to keep their eyes on both the promise it offers and the risks it brings, walking the careful path from innovation to real-world application.
Understanding 1-Octylimidazole
1-Octylimidazole pops up most often in chemical conversations about specialty molecules. This compound, made by attaching an eight-carbon octyl chain to an imidazole ring, has found real usefulness beyond the lab. Sometimes, its name doesn’t ring a bell for folks outside chemistry, but its impact shows up in surprising places.
Role in Making Ionic Liquids
One way I’ve seen 1-octylimidazole put to work is in the production of ionic liquids. These weird and wonderful liquids don’t evaporate like water, and they don’t catch fire like gasoline. Instead, they help chemists create solvents for all sorts of jobs, including cleaning up metals and running special reactions that just don’t behave in water or oil. Companies running extractive metallurgy or battery research often prefer compounds with the structure of 1-octylimidazole, since it offers both chemical stability and the ability to dissolve a whole range of unusual substances.
Applications in Organic Synthesis
Synthesis isn’t just a word for the chemistry nerds. Any time you see a new drug or advanced material, someone pieced it together step by step. 1-Octylimidazole works well as a ligand — think of it like a friendly hand for a metal atom. It attaches itself to metals and helps guide chemical reactions toward more useful products. This use is especially valuable in labs testing greener, more precise ways to synthesize pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, or dyes.
Benefits for Corrosion Inhibition
Corrosion messes with everything, from drinking water pipes to the hulls of ships. Over time, the wrong water or air can gnaw away at steel till it’s full of holes. Researchers have found that molecules built like 1-octylimidazole can coat metal surfaces and keep them safe from damage. The oily tail wraps the surface, and the nitrogen-rich head sticks firmly to the metal, protecting it from harsh environments. Some chemical plants rely on these types of inhibitors to avoid costly breakdowns and downtime.
Potential in Biochemistry Research
Biological applications probably don’t come to mind first, but there’s a trend toward using imidazole derivatives for developing new drugs or imaging agents. Because the imidazole ring is part of the amino acid histidine, some enzymes “recognize” molecules like 1-octylimidazole. Scientists are exploring how this compound might help design new diagnostic tools or treatments, though most of those uses aren’t ready for hospital shelves yet.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Every specialty chemical brings some baggage. Though 1-octylimidazole offers plenty of neat uses, nobody wants it escaping into waterways or ending up in food. Based on similar compounds, there’s concern about aquatic toxicity and persistence in the environment. Labs and factories handling this compound need strict procedures—closed systems, careful waste collection, and well-trained workers—to keep it where it belongs. Regulators and watchdog groups keep the pressure on for more transparency, which helps the industry step up its game on safety and environmental stewardship.
The Road Ahead
Most folks outside the chemical field don’t run into this molecule, yet its reach stretches into energy, pharmaceuticals, and industrial materials. Companies and researchers exploring 1-octylimidazole need to keep an eye on sustainability and health, just as much as innovation. Safer processes, better containment, and ongoing research into compounds with fewer environmental headaches all point toward smarter, responsible science. If people can keep balancing everyday needs with strong stewardship, there’s space for specialty molecules like this one to quietly change the game across industries.
Understanding 1-Octylimidazole’s Building Blocks
The name “1-Octylimidazole” might look intimidating, but looking at the word helps break down its recipe. The backbone, imidazole, draws chemists because of its ring structure—five spots, two of them are nitrogen, the rest are carbon. Past that, the “1-octyl” part means a chain of eight carbons gets linked to the first spot on this ring.
Figuring out its molecular formula becomes a matter of counting. Imidazole itself stacks up as C3H4N2. Fresh out of grad school, I’d scribble this on a post-it and stare at it. “Add the tail,” a colleague would say, meaning connect an octyl group (C8H17) by swapping one hydrogen for the carbon chain. So, stick that octyl group to the ring, lose a hydrogen in the process—something anyone who spilled solvents on their lab coat can relate to. Rolling it together, you get C11H18N2 for 1-octylimidazole.
Why Accuracy Over Names Matters in Chemistry
This sounds like splitting hairs, but confusion over molecular formulas can cause mistakes not just for researchers but for early-stage industrial work or even in a teaching lab. It’s easy to trust a supplier’s label, yet even tiny errors ripple out—one wrong letter could mean designing the wrong synthetic route, or worse, logistics nightmares in pharmaceutical manufacturing. The cost of correcting these mistakes builds up.
For undergrads or new hires in the lab, wrapping your head around why a simple octyl chain alters both the chemistry and the formula drives home that lesson—every atom accounted for. In 2007, a team at the University of California got publicly called out for reporting the wrong compound scaffold in a paper, and it cost them credibility. Experiences like that stick. The industry depends on researchers being transparent and careful, or drug trials, material science, and basic biochemistry all suffer quality setbacks.
Beyond the Formula—Why the Structure Gets Attention
Some chemists focus on structure as well as formula, because swapping a hydrogen for a bulky tail means the compound could dissolve differently, bind to proteins in odd ways, or resist breaking down in the environment. As someone who’s tinkered with imidazoles for corrosion inhibitors, seeing the octyl side chain nudges me to ask: will it increase lipid solubility? Could it cross barriers in cells, or act differently once it hits a real-world system?
That’s the heart of research—building off the backbone and asking new questions. The exact nature of C11H18N2 can determine whether a scientist uses it for ionic liquids, antimicrobial testing, or as a base for more complex compounds. People reading product specs or journal articles deserve to know exactly what they’re getting. That accuracy prevents resource waste and safety slip-ups.
Ways Chemistry Can Cut Out the Guesswork
Lab teams stress double-checking: peer review, running NMR and mass spec, and using open-access repositories to keep the data transparent. Some start their syntheses with a paper trail that tracks each step, so mistakes are easier to spot. Standardizing how these formulas get reported, especially in digital catalogues, would head off mismatches between what’s ordered and what’s delivered.
Every person—chemist or student—should get used to working through structures, not just copying from a database. Attention to this detail over time boosts the reliability of every experiment and every batch sent out to factories or research institutions. For a clear-headed approach, the formula for 1-octylimidazole stands as a model of chemistry’s need for accuracy, one easily verified and widely referenced as C11H18N2.
The Risk in the Bottle
1-Octylimidazole has become a go-to reagent in organic synthesis, surface chemistry, and some ionic liquid production. Its long carbon chain and reactive imidazole ring sound innocent on paper, but people in the lab know a chemical doesn’t care how harmless it looks. Taking care around this stuff isn’t just a box to check; it can save your skin — literally.
Personal Protection Makes the Difference
PPE is a daily companion. Splash goggles, not just prescription safety glasses, help keep fumes and droplets away from the eyes. Disposable nitrile gloves give decent resistance for common spills, but the material can soak through quicker than you think, especially if hands end up in contact for more than a few minutes. A lab coat handles splashes, but a chemical-resistant apron adds another barrier if you’re pouring bigger volumes. Respirators can come up if you’re generating vapor or don’t have good ventilation, but that’s rarely the case for small-scale bench work with this type of compound. Still, you want to work in a fume hood every time, no question.
Paying Attention to Ventilation
Volatile organics ask for respect. Even without a strong odor, 1-Octylimidazole vapors can run up exposure before you notice. Fume hoods are there for a reason. Running procedures with the sash down low makes a world of difference if a reaction runs hot or you get hit with an unexpected release. Simple room fans or cracked windows don’t keep you safe — protecting your lungs means sticking to professional equipment built for chemical work.
Keeping Clean Matters
Chemicals stick around. After handling 1-Octylimidazole, washing hands with soap and water cuts down the risk of tracking residues onto doorknobs, phones, or your face. Benchtop liners and absorbent pads don’t just keep the space neat; they prevent a small drip from becoming a bigger workplace hazard. Spill kits should be stocked and ready, with enough material to contain and neutralize the kind of mess that actually happens, not just brochure-sized spills.
Storage: Think Beyond the Label
I’ve seen folks toss imidazole derivatives onto a random shelf. This invites trouble. Sealed glass bottles with tight-fitting caps cut down leaks and vapor escapes. Storing away from acids, oxidizers, and strong bases in a cool, shaded space keeps the chemical stable. Flammable cabinets offer peace of mind if your lab heats up. Don’t rely on memory — clear labeling and a chemical inventory help on busy days when everyone’s grabbing supplies and it’s too easy to confuse similar bottles.
Training and Accountability
Lab safety isn’t about reading posters. Someone who’s new to handling 1-Octylimidazole learns best with a rundown from veterans. Demonstrating how to clean up a real spill, or what to do if someone catches a splash on their skin, makes the lessons land. Everyone should know where the safety shower and eyewash are, and it helps to practice — not just read an SOP. Emergency contacts posted on the door mean even a visitor can call for help fast.
Better Habits Today, Safer Labs Tomorrow
The lab is no place for shortcuts, and good habits build the kind of environment where everyone goes home healthy. Well-designed protocols and staying sharp help everyone focus on discovery rather than damage control. With chemicals like 1-Octylimidazole, real safety takes routine effort — and that effort pays off every day.
Why Proper Storage Matters
People working with chemicals understand the risks tied to sloppy storage practices. I’ve seen both small-scale and big labs make the mistake of treating a bottle like salt or sugar, not recognizing the hazards some substances bring. 1-Octylimidazole doesn’t announce itself with a big “danger” label in everyday use, but mistakes stack up quickly without careful treatment.
Understanding 1-Octylimidazole’s Properties
1-Octylimidazole stands out because of its unique molecular structure—part imidazole, part long-chain alkyl group. That means it’s not like your average short-chain solvent. This stuff absorbs moisture from the air and reacts with some oxidizing agents. In badly ventilated places, or when left in direct sun, the substance can change over time, breaking down, ruining purity, and posing risk to whoever works with it next.
What Works in Real Life
I’ve seen a few solid storage methods that make a difference. Use tightly sealed glass bottles with well-fitted lids. Avoid plastic that gets soft or reacts over time. Place the bottle in a dry, cool spot away from heat, not just on a random lab bench or close to a sunny window. Drive home the point: temperature swings speed up chemical changes. Heat destroys stability and, in rare cases, the mix becomes too risky to touch.
People need to read and follow recommended storage temperature ranges. For 1-octylimidazole, keeping it at or just under standard room temperature extends shelf life and keeps batches usable. Humidity control deserves special mention. Sometimes staff forget that a cap left loose—even for an hour—lets in just enough moisture to ruin a batch. Best practice uses desiccators or silica gel packs if the room gets humid. I always check storage rules after any change in the lab setup. Too many people wing it and only realize the problem once chemical breakdown starts.
Risks of Ignoring Guidelines
The accident reports tell a clear story. Bottles stored above heat vents, or beside chemicals that react with each other, lead to batch failures and dangerous working conditions. Even worse, unstable compounds can trigger fires, especially with containers near flames. Once, I met a researcher who dropped a bottle after handling it with wet gloves. Small mistakes pile up, and not knowing the risks puts entire projects and people at risk.
Safe Handling Culture
Proper labeling forms the backbone of a trustworthy system. Every bottle must show a clear date so older bottles don’t sneak back into use. Supervisors can set the tone by making safety a visible, daily priority. I remember a supervisor who insisted everyone double-check seals and storage records each week. It took five minutes but paid off in peace of mind and safe results. New staff members should get a walkthrough of the chemical storage area on day one—safety rules sink in fastest through consistent practice, not just reading a page of protocol.
Moving Toward Best Practice
Simple steps cut risk: pick the right container, label it clearly, store away from hazards, and train everyone well. Respect the chemical you work with, or you deal with the fallout later. Time invested in better storage saves headaches, money, and sometimes much more. I learned that paying attention to details around chemicals like 1-octylimidazole builds trust and safety for everyone in the lab.
Why Purity Counts in the lab and on the Shop Floor
1-Octylimidazole doesn’t show up in conversations outside of specialty chemistry, but for those who work in research, pharmaceuticals, or materials science, every decimal point in its purity can change outcomes. Small impurities end up altering results in sensitive reactions, shifting a carefully-planned process into an unknown experiment. No one wants to redo weeks of work because a solvent or catalyst escapes quality checks. Having spent hours troubleshooting puzzling inconsistencies in data, I know the frustration when you realize contaminated starting material escaped your notice.
Understanding What’s on Offer: Not Just Numbers
In practice, most suppliers offer 1-Octylimidazole at a purity grade above 97%. Some stretch that to 98% or even 99% for demanding needs. The landscape usually splits between “purified” and “analytical” (or “high-purity”) options, with prices and lead times to match. Analytical-grade batches fit best for analytical chemistry, trace analysis, or anything needing little uncertainty from contaminants. If your application lands in nanomaterials or organic electronic devices, chasing after the purest variant makes sense. Low metal content also enters the checklist for electronics, as trace metal ions play havoc in sensitive circuits.
Pharmaceutical researchers look for certificates of analysis as proof, not just a sticker on a bottle. I’ve been in rooms where a 0.5% increase in purity could mean the difference between a reproducible trial and a regulatory red flag. The paperwork tells you what solvent residues, water content, or side-chain byproducts sit in the blend. If a vendor skips details, that’s a red flag.
Supply and Demand: Not Every Catalog Looks Alike
It’s easy to forget how much supplier location, regulation, and demand shape what’s available. Europe’s REACH guidelines force a closer look at contaminants. Suppliers from the US and Japan tend to list more information, likely owing to tighter local oversight and active R&D markets. Smaller companies sometimes offer custom purifications for a price, but that comes with longer waits and less guarantee on batch-to-batch consistency.
Sometimes the real challenge starts once the bottle arrives. Few labs own state-of-the-art instruments to reconfirm supplier claims, especially for subtle organics. If funding is tight, researchers face a dilemma: trust the label or run extra quality control tests and lose precious time. That adds stress, especially in fast-moving product development.
Pushing for Better Access and Standards
Big picture, reproducibility in science depends on chemical purity. Unpredictable variations lose value for everyone. Industry-wide, it’s in everyone’s interest to press for more detailed certificates and batch traceability. Tracking specific lot numbers, double-checking purity using techniques like NMR or HRMS, or even pooling resources on in-house validation could help reduce headaches down the line. Collective demand for transparency leads suppliers to tighten their own process controls, resulting in less wasted effort, less confusion, and results everyone can trust.
The nitty-gritty of purity grades for 1-Octylimidazole rarely hits front pages, but anyone who’s ever lost precious hours to an unexplained anomaly knows the real-world cost. Attention to these small details means fewer reruns and fewer doubts about the chemistry powering tomorrow’s breakthroughs.