Ethyl 4-Chlorobutanoate: Practical Insights, Progress, and Real-World Relevance
Historical Development
Chemists started working with alkyl esters like ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate in the mid-20th century during the rise of organic synthesis as a core field in modern chemistry. The push towards more efficient, versatile building blocks in pharmaceuticals and materials created a space where this compound rose from bench-scale curiosity to a regularly used intermediate. Early workers saw the straightforward reactivity of the 4-chloro group, as well as the robustness of the ethyl ester, and realized the value in simple modifications. This simplicity favors learning in the lab and pushes industrial chemists toward deploying it in process routes, since mistakes or waste show up quickly.
Product Overview
Ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate entered the market as both a research reagent and an intermediate in larger chemical recipes. The product typically appears as a colorless to pale yellow liquid, often stored in tightly sealed bottles away from light to avoid unwanted degradation. Commercial stock comes in various purities, but for the kinds of reactions used in medicinal chemistry or fine chemicals, purity above 97% usually satisfies most needs. Its shelf stability and straightforward storage requirements turn it into a workhorse for chemists, rather than a specialty item that demands much oversight.
Physical & Chemical Properties
The ester boils around 86-88°C at 15 mmHg and displays a density close to 1.07 g/mL at room temperature. Its molecular formula C6H11ClO2 and moderate molecular weight allow for predictable manipulations in synthetic steps. The compound dissolves easily in most organic solvents like ether, dichloromethane, and acetone. That mild solubility lets researchers incorporate it in various environments without needing specialty solvents. The 4-chloro substituent, which sets it apart from its non-halogenated analogues, triggers selective reactivity, guiding alkylation or nucleophilic displacement in a predictable manner. The ester functional group stabilizes the molecule, pushing its reactive center down the chain and keeping things manageable in the flask.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate typically ships with clear specification sheets from reputable suppliers. Labels should include purity grades, water content, appearance, melting point if applicable, and storage instructions. Regulatory annotations under GHS show hazard pictograms recommending careful handling. Good quality assurance means every container comes with a batch number and expiration date, which labs and factories track for safety compliance and tracking unwanted residue or waste. Transport guidelines list UN numbers and recommend temperate storage, as extreme cold or heat can alter properties or compromise containers.
Preparation Method
A direct, hands-on method to prepare ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate starts with reacting 4-chlorobutyric acid with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst, usually sulfuric acid. The reaction happens under reflux to hasten esterification, and water formed during the process gets removed to shift equilibrium toward the ester. Chemists then extract the product into a suitable organic layer, dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and distill at reduced pressure. The byproducts—acid residue and any leftover ethanol—lower the yield if not properly managed, so practical chemists take care to optimize the ratios and washing steps to ensure purity meets downstream needs.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
The versatility of the molecule shows up in everyday lab practice. The chloride at the terminal position invites SN2 substitutions, especially with nucleophiles like thiols, amines, or alkoxides, yielding new esters, amides, thioethers, and alcohol derivatives. Its ester function allows for hydrolysis or transesterification, which is common in scale-up or diversification steps. For example, transforming it to 4-chlorobutanol by reduction, or swapping the ethyl group for other alkyls, lets chemists create libraries of related products. On pilot scale, these routes provide straightforward, high-yielding entries to more specialized compounds, particularly in synthesis of pharma backbones or specialty monomers.
Synonyms & Product Names
Across catalogs and scholarly articles, ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate appears as ethyl γ-chlorobutyrate, ethyl 4-chlorobutyrate, or its IUPAC denomination. Scientists sometimes refer to it by shorthand, like EC4B or E4CB, making tracking chemical inventories more challenging if staff members rotate. Manufacturers tag product codes for inventory management, while import/export regulations note both its chemical and trade names to avoid ambiguity during shipping.
Safety & Operational Standards
Handling the compound without keen attention to safety can bring trouble. It emits a noticeable odor, suggesting volatility, and can cause irritation on contact with eyes, skin, or lungs. Spill management relies on using gloves, goggles, and operating inside an exhaust hood. Chemists training in bench safety learn to manage all halogenated esters as if ingestion or prolonged exposure could pose health hazards. Proper waste disposal rests on neutralization and removal by licensed chemical waste handlers, since mishandling chlorinated byproducts can create both lab and environmental hazards. Regulatory agencies like OSHA, REACH, and the EPA track such compounds, urging periodic audits of workplace air and inventory supplies.
Application Area
Pharmaceutical research continually leans on ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate to build out central nervous system agents, anticonvulsants, or enzyme-modifying drugs. The simple manipulation of its chlorine group allows drug developers to dial in potency, selectivity, and metabolic stability at an early stage, without investing heavily in riskier or more complex starting materials. In addition, agrochemical developers tap into its reactivity for herbicide and fungicide intermediates. In flavors and fragrances, chemists limit its concentration, since traces in blends can make unwelcome notes, but it remains valuable as a scaffold for more palatable esters and lactones. For everyday chemical workers, the molecule feeds into polymer and specialty material research, since its halide group acts as a gateway to new functional compounds.
Research & Development
Research teams remain interested in broadening the utility of this compound, especially in catalysis, process intensification, and green chemistry. Some studies focus on solvent-free or microwave-assisted esterification routes, reducing waste and shortening reaction times. Others boost atom economy by exploring biocatalytic alternatives, using engineered enzymes to achieve the conversion of precursors under milder conditions. Scientists also pursue downstream modification—swapping the halo group for novel pharmaceutically active fragments or attaching PEG chains to improve pharmacokinetic profiles. These improvements build on the dependable chemistry of ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate, reinforcing its place as an accessible and useful starting point.
Toxicity Research
Toxicology testing flags that high-dose exposure or repeated skin contact can cause irritation or more serious health effects, probably due to the action of the chlorine substituent. Inhalation studies find that even moderate vapor levels deserve respect and prompt use of protective masks. Chronic exposure, especially in the context of industrial accidents or poor ventilation, could lead to liver or nerve issues. Modern analytical labs rely on GC-FID or HPLC to track trace levels in air and biological samples. For operational safety, the approach revolves around preemptive control—good laboratory ventilation, active monitoring, and training workers to handle unplanned exposures without panic.
Future Prospects
Ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate finds itself at the start of several innovation threads. The movement toward sustainable chemistry pressures suppliers and downstream users to develop less hazardous chlorinated reagents or to convert chlorinated waste to less harmful products. At the same time, the flexibility in molecular design ensures this compound will keep helping researchers make new breakthroughs, especially as new reactions unlock access to even more valuable derivatives. Ongoing collaboration across chemical manufacturing, environmental science, and medical research suggests a steady role for this molecule, with the potential for new, greener methods shaping its future production and use.
Why Does Ethyl 4-Chlorobutanoate Matter?
Ethyl 4-Chlorobutanoate shows up quietly in many corners of the chemical industry, and that alone invites some questions. Even if the name sounds like something out of an advanced chemistry textbook, people working in pharmaceuticals, flavors, and research labs deal with it all the time. The compound’s combination of a chlorinated chain and an ester group makes it useful as a tool for building more complex molecules. The science-world calls this “a building block.” I see it as a kind of starting point—like flour in bread making or a blank canvas for painting.
Key Role in Pharmaceutical Synthesis
Most of the demand comes from pharmaceutical companies. Sometimes people overlook what it takes to make a new medicine. Discovery rarely walks a straight line. Chemists use Ethyl 4-Chlorobutanoate to link up different molecular parts. If a new drug needs a butanoic acid backbone with a specific twist, this compound lets the researchers put together those building blocks more easily. In the hands of a good chemist, small molecules like this can mean the difference between a failed experiment and the next breakthrough.
New molecules with potential as anticonvulsants, antitumor agents, or anti-inflammatories all owe a debt to easy access to starting compounds like Ethyl 4-Chlorobutanoate. One researcher’s early-stage synthesis may lead to a new medicine a few years down the road. Without building blocks like this, discovery would crawl at a snail’s pace.
Contribution to Flavors and Fragrances
Food and fragrance makers also find a use for Ethyl 4-Chlorobutanoate. Its ester group brings out fruity, sweet notes after further processing. I’ve spoken with lab technicians who use intermediates like this to craft the sharp, bright bite in some candies or the smooth fruitiness hidden behind perfumes. You won’t see this name listed on a box of sweets, but the chemistry behind those artificial flavors often starts with building blocks like this one. What amazes me is how many familiar tastes and smells begin life in a lab, not an orchard.
Research and Industrial Testing
In academic research and process testing, scientists use Ethyl 4-Chlorobutanoate to experiment with new types of reactions. Because the molecule reacts in predictable ways, it becomes a perfect candidate for exploring new catalytic reactions or greener synthesis strategies. Safe and efficient production remains at the core of chemical innovation. Mistakes in the lab can mean costly delays or even danger. Reliable starting materials cut down on risk and help reproducibility, which leads to better results in published studies or industry reports.
Safety, Handling, and Environmental Considerations
The handling of this compound isn’t something anyone takes lightly. It has a noticeable odor and can cause irritation if spilled. Proper ventilation, gloves, and goggles all matter in labs and manufacturing plants. Toxicity information isn’t always widely available for these specialty chemicals, which makes tightly controlled storage and handling a non-negotiable priority. Carelessness not only puts workers at risk but also adds to environmental hazards.
Looking Toward Safer, Sustainable Chemistry
Safer and greener chemistry calls for attention to materials that go into products just as much as what comes out the other end. Industry and academia should seek cleaner routes for making and using Ethyl 4-Chlorobutanoate. This could mean recycling solvents, improving waste management, or designing new reactions that avoid hazardous byproducts. Increased transparency and tighter safety standards would also help. Responsible sourcing, labeling, and communication with end-users keep everyone safer, from the workers handling barrels to the researchers pipetting samples in the lab.
Ethyl 4-Chlorobutanoate: The Formula Behind the Name
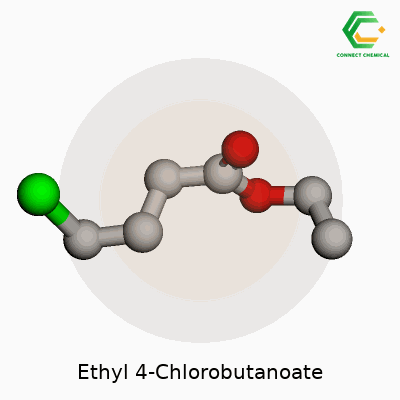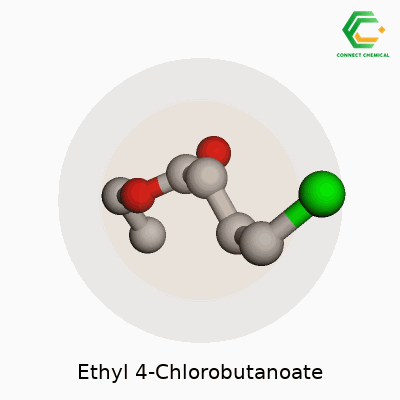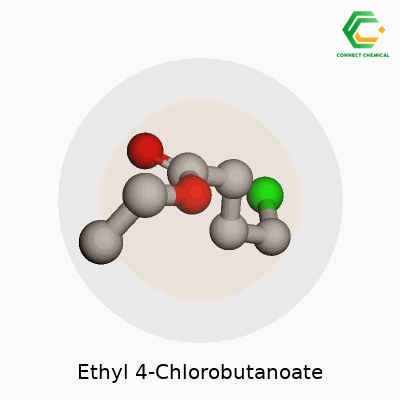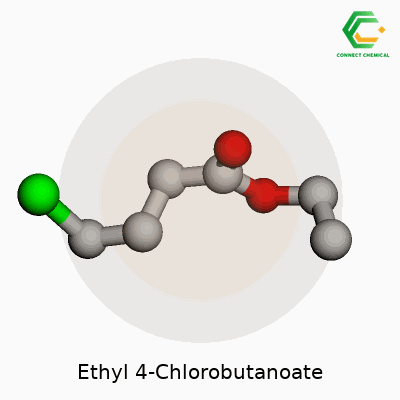
Ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate has the chemical formula C6H11ClO2. Looking at it on paper, it’s just a string of letters and numbers, but this little cluster of atoms carries a surprising amount of value in the world of chemistry. Take the butanoate backbone, add a chlorine atom in the right spot, stick an ethyl group onto the end, and you get a compound that shows up in a lab a lot more often than most people realize.
Why Care about Simple Chemical Formulas?
Names like ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate pop up in industrial and pharmaceutical labs, where small changes at the molecular level can affect how drugs act or how specialty chemicals are made. The “4-chloro” part of the formula means there’s a chlorine atom sitting on the fourth carbon of a butanoic acid skeleton. Think of it like modifying a Lego structure: snap a small piece on the side, and the entire model suddenly does something new. The ethyl piece is an alcohol-based tail hooked onto the acid, flipping the script on how the molecule reacts during synthesis.
Real-World Impact and Why the Formula Matters
For anyone who’s worked with esterification (the reaction that gives us ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate), it’s clear why exact formulas matter. Forget a hydrogen here or there, and you might end up with a totally different molecule, useless for the job you’re trying to do. In pharmaceutical work, that slight difference can make or break a drug’s effectiveness—or even turn something beneficial into something harmful. According to the FDA, controlling impurities and verifying ingredients play essential roles in drug safety. If a company reports the wrong formula or misses a single element, a batch can get recalled and patients’ health can be put at risk. From an environmental standpoint, the placement of a chlorine atom controls whether the compound breaks down easily or lingers in soil and water. Incorrect disposal of halogenated compounds like this one leads to persistent organic pollution, a concern that environment-related agencies often highlight.
Quality Control and Research Integrity
Experience in the chemical industry shows that verifying chemical formulas isn’t just busy work. Each time a new synthesis or process begins, technicians and chemists run quality control checks on each step—infrared spectroscopy, chromatography, and sometimes even NMR scans. These aren’t overkill; they’re insurance. Labs want to know that all atoms are where they belong. Misidentification at this stage can waste resources, create dangerous by-products, or stall research. Integrity starts with the basics, like getting C6H11ClO2 right and goes all the way up to ensuring ethical research that won’t damage reputations or health.
What Can Be Done Going Forward?
Education makes a difference. Chemistry students who treat formulas as more than rote memorization step into the lab with respect for what those notations symbolize. Strong protocols—double-checking reactants, keeping up with safety guidelines, and verifying supply chain sources—build a safer environment not just for scientists but for people who use chemical products daily. Input from regulatory agencies and open access to accurate structural information also help keep companies honest. As science keeps moving, careful attention to detail in the little things—like writing C6H11ClO2—sets a foundation for safe, responsible progress.
Why Storage Matters in the Real World
Few people outside labs and chemical plants think much about chemical storage, but one slip can cause lasting trouble. Ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate, an ester used in flavors and fragrance chemistry, doesn’t tolerate neglect. Leaks or fire risks might sound like textbook warnings, but anyone who’s cleaned up a spilled bottle can tell you—these risks show up fast. Protection isn’t about ticking boxes for inspectors. It’s about keeping people and places safe enough to work another day.
The Risks Behind the Bottle
This compound carries a sharp, sweet smell. It can irritate skin and eyes, and releases fumes that get worse if the air doesn’t move. Take a whiff too close, headaches and nausea sometimes follow. Flammability ranks high on the worry list, so careless storage trades short-term convenience for long-term headaches—literally and legally.
Practical Storage Strategies
Always go for a cool, dry spot, far from sources of heat or flame. Sunlight increases pressure inside bottles, which can make caps pop or containers burst. Nobody enjoys the surprise of a chemical-soaked mess in a storage room, and fire codes exist for a reason.
Ventilation matters. Fumes that hang around increase the odds of problems. Use metal cabinets designed for flammable chemicals. These aren’t cheap, but they shield from sparks and slow fires. I’ve seen places cut corners—using leftover kitchen cabinets or stashing bottles behind supplies. Sooner or later, those shortcuts violate trust with everyone who shares that space.
Keep Ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate in its original container, tightly closed, with a clear label. Swapping to unlabeled bottles invites confusion, mistakes, and dangerous mixes. Mix-ups get more likely during long projects or staff changes.
Fighting Moisture and Contamination
Desiccants tucked near storage areas soak up stray moisture. Water reacts with esters, sometimes setting off foul odors or even slow, corrosive reactions. People who’ve coped with sticky residue or spoiled product know that drying agents don’t cost as much as throwing away ruined stock.
Never store this compound near acids, bases, or oxidizers. Accidental mixing starts chemical reactions that boil, smoke, or eat through shelves. Check shelves regularly—signs of leaks, cracked lids, or crusty residue hint at deeper problems. Safety data sheets read like overkill until the first incident. Then, every line makes sense.
Community and Responsibility
People sometimes skip best practices during busy stretches, especially in smaller shops or schools. Years spent working with chemicals taught me: it doesn’t take a PhD to follow instructions, just a little respect for what’s inside each bottle. Share tips with coworkers, and build habits so safety becomes routine, not a chore.
Basic investment in chemical training and regular checks keep disaster at bay. Reputable suppliers provide safety data and help troubleshoot issues—don’t let cost-cutting decisions drive risky storage. Protecting people and reputations should outweigh every shortcut.
Building a Stronger Safety Culture
Good storage of ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate demands more than rules on a page. It’s a lived practice, shaped by care, vigilance, and teamwork. Safer habits make the difference between quiet days and emergencies that echo for months.
Everyday Work and Safety Questions
Anyone who works in a lab or a busy industrial plant runs into chemicals with long names all the time. Ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate is one such chemical. It doesn’t sound famous or glamorous, but questions about its safety show up often. People wonder if it’s hazardous or toxic, and for good reason. Even chemicals used in tiny amounts can raise big safety concerns if handled carelessly.
Chemical Profile and Workplace Concerns
Ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate falls into the category of organic esters. It's a colorless liquid with a fruity odor, popping up in pharmaceutical and flavor manufacturing. I’ve seen containers with its label on them in tightly regulated storage rooms. Reading the safety data sheet always paints a clear picture: Liquid contact with skin can cause irritation and even burns. Vapors irritate the nose and throat. Breathing those vapors—especially at higher concentrations—leaves you feeling off. If a spill happens, the area needs quick cleanup and proper gear.
Poor Handling and Health Dangers
Nobody wants to spend a shift with red, itchy skin or a cough that won’t quit. Cases of exposure to Ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate have sent workers to medical units. The American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists lists it as an irritant. Accidental splashes in the eyes send people scrambling to emergency eyewash stations. Long-term exposure rarely makes headlines, but the cumulative damage matters. Over the years, I’ve seen that folks who skip gloves or masks sometimes develop chronic issues. Symptoms like headaches or dry cough show up in environments where ventilation isn't up to par.
Fire Risks and Spills
This liquid catches fire, so storage is no afterthought. In hot climates or near open flames, it evaporates quickly. The fumes can ignite and trigger larger accidents. I still remember a fire drill set off by a leaky bottle in a stuffy storeroom. Emergency crews dealt with it fast, but the lesson stuck: Storing volatile chemicals with open flames or heat isn't worth the risk.
Facts That Matter
Regulatory bodies—including OSHA and the European Chemicals Agency—have marked Ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate with clear hazard statements. It harms if swallowed, inhaled, or if it touches skin or eyes. It rarely kills outright, but the risk is real if you ignore the basics. Short-term exposure often brings mild symptoms; higher doses or repeated contact can result in more serious effects. Most calls to poison centers about it come from accidental handling, not intentional misuse. Animal studies suggest toxicity, so extra caution in workplace settings makes sense.
Stronger Culture of Safety
It’s tempting to cut corners on personal protective equipment when projects pile up. Direct experience shows that quick tasks without gloves and goggles turn into accidents as soon as distractions creep in. Good training and strong leadership do even more than labels and warning signs. Decent extraction fans, eye-wash fountains, and marked storage spaces limit emergencies. At a basic level, asking simple questions like “Are the fumes strong?” or “Will my hands get wet?” keeps danger in check.
Better Communication and Education
Chemists and technicians rely on each other to spot risks and speak up before accidents happen. Real training includes hands-on drills, realistic scenarios, and the freedom to pause work if something feels off. Checklists and quick monthly reviews keep everyone honest. Management teams who see health and safety as a daily practice—not a quarterly bullet point—run workplaces where people rarely get hurt by Ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate or any other irritant chemical. Clarity saves skin, lungs, and lives.
Ethyl 4-Chlorobutanoate Purity—Why Precision Matters
I’ve seen labs attempt great syntheses, only to trip over impurities others barely notice. In jobs where chemical products transfer from one bottleneck to the next—medicines, fragrances, specialty polymers—purity turns out to be more than a number. For ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate, ignoring this can mean ruined batches, lost time, and a snowball of downstream headaches. So let’s talk facts and the practical side of setting and checking purity specification.
Common Industry Purity Benchmarks
Ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate often lands on a chemist’s desk at 98% or higher purity by gas chromatography, measured against reputable reference standards. Pharmaceutical work or advanced synthesis typically pushes for a minimum of 99%, shrinking allowable impurity content to trace amounts. Technical grades intended for less sensitive operations sit lower, around 95%, but never below—straying from that threshold throws open the door to unpredictable reactivity.
GC analysis, with attention to the height of the main peak compared to minor ones, provides the numbers that drive purchase or rejection decisions. Reliable suppliers offer full chromatograms and impurity lists, not only an overall mean value for ‘purity’. That transparency distinguishes vendors committed to protecting reputations, not just bottom-line sales.
Risks Hiding in the Details
I once watched a production batch of an intermediate derail overnight—not from human error, but a single contaminant above the 0.5% guideline. That impurity slipped in from a loose tolerance during raw material shipping, and the financial consequences rippled through budgets for months. Residual solvents, unreacted starting material, or byproducts such as 4-chlorobutyric acid or ethyl butanoate cut into ideal yields or trash product profiles. Some of these slip past routine analysis unless people look close.
A tangled aroma, reduced shelf life, or a tinge of color in a typically colorless liquid might seem minor in training but end up defining product quality for a customer with strict specs. The pharmaceutical crowd keeps a special eye on genotoxic or carcinogenic impurities, for instance, which must sit below the lowest practically achievable levels—often below 0.1%.
Transparency, Testing, and Gathering Trust
Reading a certificate of analysis rarely offers the whole picture. Visiting supplier sites and following their process for verifying batch purity reveals more—the conversation makes room for questions about test frequency, equipment calibration, and how non-conformances get caught early. Suppliers tend to win business not by ducking hard questions but by laying out the data, including the profile for water, acidity, and even the method validation results.
Analytical methods shift with the times, too. GC with flame ionization stood out a decade ago, but today, buyers lean on GC-MS and NMR to dig deeper into minor impurities. Laboratories invest in these capabilities also because regulatory pressures climb. Agencies like the FDA and EMA don’t leave much room for fuzzy math, especially with anything threading toward an API.
Setting the Standard for Safe and Reliable Synthesis
Consistent, validated purity means predictable chemistry. I’ve found that making purity results and analytical methods readily available, not hidden behind ‘proprietary’ screens, builds trust with partners faster than any high-gloss marketing sheet. Simply hitting the spec for ethyl 4-chlorobutanoate saves more than a product—it shields a company’s name, employee jobs, and in some industries, public health. Keeping the standard high isn’t just for compliance—it proves a supplier’s word means something.