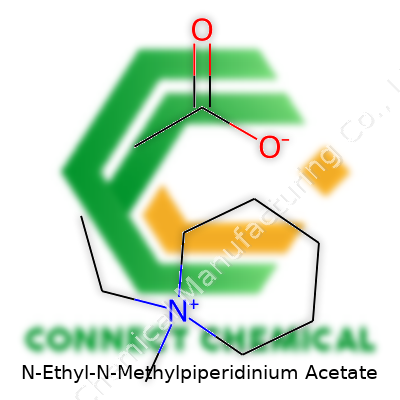
N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate: History, Properties, Uses, and Prospects
Historical Development
The story of N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate traces back to the broader history of quaternary ammonium compounds, which chemists began to explore seriously in the mid-twentieth century. Early research into piperidinium salts started with medicine and organic synthesis in mind. Over time, advances in purification, analytical chemistry, and a growing toolkit for synthetic organic reactions placed more exotic salts on the chemist’s radar. Somewhere along the line, researchers added N-ethyl and N-methyl groups onto the basic piperidine scaffold, explored how these tweaks affected the molecule’s behavior, and found that coupling the cation with an acetate anion created a new material with new properties worth noting. This step allowed the compound to emerge as an option for both industrial applications and specialized laboratory work. As researchers tuned ionic liquids and needed new supporting electrolytes, N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate became a notable player in a growing catalog of designer salts.
Product Overview
N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate stands out as a member of the quaternary ammonium family, featuring a six-membered piperidine ring substituted with methyl and ethyl groups. Once combined with the acetate anion, the resulting salt offers not only ionicity but also chemical and thermal stability hard to find in other comparable options. Producers typically market this substance in its pure crystalline form or dissolved in suitable solvents for advanced experimentation. The number of uses grows every year, from electrochemistry and catalysis to a few areas in pharmaceutical intermediate preparation and analytical testing. A lot of interest currently comes from the compound’s role in enabling clean, high-efficiency separations in both laboratory-scale and pilot-scale settings.
Physical & Chemical Properties
A standout feature—at room temperature, the solid is white to slightly off-white and absorbs moisture from air, so keeping it sealed up really matters. The melting point usually lands in the range you've come to expect from ionic salts, staying solid at typical workbench conditions. As a salt, it dissolves in water and many polar organic solvents, forming colorless solutions. Researchers studying its structure find strong ionic interactions tying the cation and anion together, leading to decent solubility, but also a robustness in non-aqueous environments. Since it holds a nitrogen atom fully substituted by carbon chains, there’s not much reactivity from the amine itself—most of the chemistry happens at the anion, which likes to engage in hydrogen-bonding. This trait opens up a great deal of flexibility for reaction designers.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Suppliers list N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate with purity percentages, generally exceeding 98% for research grades. Identifiers like CAS numbers, batch number, and shelf-life are clearly marked on packaging. Companies involved in regulatory compliance assign GHS pictograms to indicate handling precautions and align safety data with international guidelines. Specifications go further, covering trace impurities, precise melting points, water content, and, if appropriate, heavy metal concentrations. Analytical verification includes NMR and infrared spectra with certificates of analysis. Packaging gets selected to minimize moisture ingress, often using amber glass vials or HDPE bottles, sealed tightly to preserve product quality. Clear labeling lets users quickly see if storage temperature or light protection is required, and hazard statements warn technicians about possible risks without relying on jargon.
Preparation Method
Most syntheses start by alkylating piperidine, first with a methylating agent, then with an ethylating reagent. The resulting N-ethyl-N-methylpiperidinium compound pairs with acetic acid or an acetate salt to finish the job. Chemists keep reaction temperatures low to control byproduct formation. Purification involves crystallization or extraction, followed by drying under vacuum or in a desiccator to avoid humidity issues. Modern approaches introduce greener solvents to minimize waste, and scalable procedures let suppliers produce both small batches for research and multi-kilogram lots for industrial use. Each step, from initial alkylation to final salt formation, demands careful monitoring, since subtle changes in conditions can produce impurities that complicate later applications.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
The molecule’s core stays largely unreactive in moderate conditions, but the acetate group provides a reactive handle. Chemists have used it as a base, nucleophile, or ligand in specialized organic reactions. Swapping out different acid partners opens the door to analogues with different anions, each tweaking solubility and reactivity for a broad array of tasks. Under stronger conditions, the piperidinium ring can participate in ring-opening reactions, though most lab work avoids extremes that could break the molecule down. Some studies test substitution on the alkyl groups, but wholesale modification shifts the compound into new chemical territory, making these more than just minor tweaks.
Synonyms & Product Names
Trade names don’t show up often for this salt; chemists call it by its systematic name, N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate, or abbreviate as EMpA. It also appears in research as 1-ethyl-1-methylpiperidinium acetate or uses short forms like MeEtPipOAc in laboratory logs. Some suppliers group it with “ionic liquids” or “quaternary ammonium acetates,” so recognizing both common and systematic nomenclature helps avoid confusion when sourcing or reading literature.
Safety & Operational Standards
This compound, like other quaternary ammonium salts, shows low volatility and doesn’t cause major inhalation concerns during ordinary lab work. Still, direct contact can irritate eyes and skin, and ingestion or prolonged exposure leads to discomfort. Industry-standard protocols call for gloves, goggles, and lab coats at a minimum. Any spills get cleaned with copious water and collected for safe disposal. Facilities install local ventilation to capture any dust or mist. Waste disposal teams send residues for incineration or chemical digestion, not down the drain. Safety datasheets remind researchers of acute toxicity testing results, and laboratory trainers emphasize routine handling precautions in every training session.
Application Area
Most industrial users put N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate to work in electrochemical setups, such as as an electrolyte component for specialized batteries or capacitors, where its ionic conductivity and chemical stability outperform older salts. Process chemists in synthetic labs deploy it as a phase-transfer agent or reagent for organic transformations, chasing higher yields and cleaner separations. Some teams in separation science experiment with this acetate for extracting target compounds from complex mixtures, especially where traditional ionic liquids fall short. Academic researchers tinker with blends, aiming to unlock new solubility regimes or push selectivity in catalysis beyond what traditional ammonium salts offer. Pharmaceutical manufacturers see potential in advanced stage syntheses, since the compound offers relatively predictable behavior during high-pressure or high-temperature reactions.
Research and Development
Ongoing R&D focuses on adapting N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate for greener, safer, and more energy-efficient processes. Teams explore combinatorial approaches, pairing the salt with other ionic liquids to create custom solvent systems for difficult industrial extractions and synthetic challenges. Electrochemical engineers run head-to-head comparisons with more established salts in new battery designs, testing for cycle stability, leakage resistance, and compatibility with new electrode materials. Environmental researchers collect data on the compound’s breakdown products and rates under different pH and temperature conditions, hoping to better constrain long-term impacts of accidental releases or disposal. Pharmaceutical research checks impurity profiles when this salt acts as a base or phase-transfer catalyst at production scale. Academic publications appear each year tracking progress on modifications to either the piperidinium backbone or the anion, with every new tweak yielding insight into how molecular structure steers performance.
Toxicity Research
Toxicologists place N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate in line with other quaternary ammonium salts for acute and chronic effects—limited absorption through skin, mild irritant to eyes and mucous membranes, and moderate oral toxicity if large quantities are ingested. Dose escalation studies in lab animals find threshold effects at much higher concentrations than workers would typically handle, offering some margin of safety if basic operational controls are in place. Environmental fate studies look for bioaccumulation and rate of degradation in water and soil, concluding that the acetate ion helps the compound break down more readily than some halide-based relatives. Still, persistent residues call for careful management after large-scale use, and plans for long-term monitoring support both workplace safety and environmental stewardship.
Future Prospects
Interest in new battery chemistries and energy storage technology fuels much of today’s curiosity about N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate. Better-performing electrolytes form the backbone of next-generation devices, and this salt offers a combination of high conductivity, manageable viscosity, and decent electrochemical windows. Aside from electronics and energy, fine chemical and pharmaceutical companies expect to see growth in phase-transfer systems powered by these ionic liquids. Green chemistry pushes for more recyclable and less toxic solvents, and modifications of this molecule could help bring industry closer to that ideal. Machine learning and computational modeling keep speeding up screening of new analogues, helping predict which derivatives might handle targeted applications even better. Whether for lab experimentation or process scale-up, demand keeps growing for materials that blend safety, performance, and regulatory acceptability—all areas where N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate holds a strong hand.
Understanding Its Role Across Industries
N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate has caught the eye of chemists and engineers alike, and for good reason. This compound steps beyond being just another entry in a dense chemical catalog. People turn to this material for its strong performance in ionic liquid research, battery design, catalysis, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. Each of these areas faces real challenges that N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate helps solve.
Powering Next-Generation Batteries
Rechargeable batteries sit at the center of our lives, from powering electric cars to hidden inside smartphones. Poor electrolytes choke battery capacity and lifespan. Scientists searching for safer, longer-lasting battery fluids landed on ionic liquids as one answer. N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate, thanks to its low volatility and thermal stability, offers a safer option than many flammable, toxic solvents. Lithium batteries built with it run cooler, rarely catch fire, and lose less charge over time. Major research teams have shown that piperidinium-based ionic liquids support greater charge cycles compared to conventional electrolyte salts.
Green Chemistry and Catalyst Systems
Traditional solvents raise eyebrows because of health and environmental concerns. I’ve watched researchers in labs glove up to handle nasty chemicals, always worrying about spills and fumes. Ionic liquids give people safer alternatives. N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate stands out for being stable, easy to handle, and less hazardous. In catalysis, chemists use it as both a medium and a participant in reactions. It often helps reactions run at lower temperatures or with fewer byproducts—a big win for sustainability. For example, its use in the synthesis of fine chemicals and active pharmaceutical ingredients underscores a shift toward greener processing, as reported in several peer-reviewed journals.
Extraction and Separation Processes
Industries need ways to pull out valuable materials from waste streams or raw mixtures. Ionic liquids offer new methods for separating metals, recovering rare earth elements, or extracting organic compounds without heavy, polluting solvents. N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate, with its selective solubility, lets engineers pick out specific components with better yields. Studies have reported better performance in extracting heavy metals or radioactive contaminants from water using this compound than with traditional extractants.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Drug companies look for ingredients that improve performance and safety. N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate serves as an ionic liquid supporting safer and more efficient drug synthesis. Not all solvents fit the demanding standards of pharma, but this one checks boxes like low flammability, reduced toxicity, and chemical inertness. In my work with process chemists, I’ve seen batches lost to poor solvent choices—switching to ionic liquids like this one often leads to cleaner, more reliable outcomes. The FDA’s continued scrutiny of solvent residues also pushes firms to consider options with cleaner profiles.
Challenges and Moving Forward
Despite all these strengths, engineers sometimes shy away from ionic liquids because of price and the lack of “long-term” data on environmental breakdown. Cost drops as production grows, and researchers keep testing these compounds for biodegradability. Government funding into new battery chemistries and green solvents points to a future where N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate appears in more everyday products—changing the way people think about energy, manufacturing, and environmental care.
The Molecular Makeup
N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate brings together a distinct set of atoms. Its chemical formula, C10H21NO2, reveals this blend: a piperidinium core with both ethyl and methyl groups attached, pairing up with an acetate anion. The molecular weight clocks in at 187.28 g/mol. It’s a mouthful at first, but behind the formula lies a growing place for these compounds in today’s labs.
Not Just for Chemistry Geeks
Down on paper, it looks like just another structure out of a thick textbook, but walk into any research lab and you’ll hear about the rise of ionic liquids. N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate falls straight into this growing class. While ionic liquids used to sound exotic, researchers have shown that swapping out traditional volatile organic solvents with these salts can change the game. Ionic liquids like this one come with low vapor pressure and good thermal stability—basic requirements for safer chemistry.
Green Chemistry Drives the Market
Back when I worked with solvents, the stink and hazards were constant reminders of their environmental cost. Swapping to ionic liquids saw me checking off fewer safety warnings and storage headaches. Chemists have published studies highlighting how these salts help reduce emissions. The acetate ion gives this compound its solubility with water and its capacity to dissolve many types of materials. Even so, the specific piperidinium structure in N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate means lower flammability and more chemical resilience compared to earlier ionic liquids based on imidazolium or pyridinium.
Navigating Production and Supply
Producing these compounds still takes care. Many syntheses rely on quaternization reactions, with yields depending on clean feeds and careful reaction conditions. Small impurities or leftover reactants can cause headaches down the line. From my experience, consistent product purity depends on skilled technical oversight in the plant—not just faith in automation.
Where to Use It Today
Energy storage stands out as a fast-growing area for these compounds. Electrolytes in new-generation batteries, particularly in all-solid-state configurations, need salts that don’t break down easily when charged up. Academic and corporate teams have shown ionic liquids boost stability and operational life in lithium and sodium battery prototypes. I’ve read reports from battery startups aiming to swap out old carbonate solvents for ionic liquids like N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate to cut down on flammable ingredients.
Trouble Spots and What Could Fix Them
Production scale and raw cost still hold these compounds back. Cheap solvents remain the first pick for most large factories. For these ionic salts to reach bulk manufacturing, better catalytic routes and recycling strategies could shrink the price gap. Waste management needs its share of attention, too. Some new ionic liquids have raised concerns because of persistence in the environment. Companies and researchers need to keep tabs on breakdown products, testing their toxicity over time.
Building Trust and Expertise
High-quality data matters as much as flashy chemistry. Real-world safety sheets, published toxicity assessments, and genuine performance data set trustworthy sources apart from misleading ones. Labs, industry users, and suppliers all have to keep transparency at the center, especially with newer compounds.
Safety Starts with Small, Consistent Actions
Anyone who has spent time around chemical storage knows that skipping the basics leads to accidents. Every day, warehouses, labs, and even classrooms juggle dozens of substances. N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate falls into the growing category of ionic liquids—a group prized in industry for their low vapor pressures and use as solvents. Even so, risks don’t disappear just because fumes aren’t filling the air. Quite the opposite: when problem signs aren’t obvious, it’s easy to grow careless.
Understanding the Stuff You’re Storing
Experience tells me the first rule: always know the enemy, or at least the material you’re working with. N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate, while not as notorious as some acids or bases, still holds the potential to irritate skin, eyes, and airways. The data sheet—the one usually buried in a binder or downloaded months ago—provides a road map. Look up melting and boiling points, flash point, and stability with common materials. The information you need hides in those boring blocks of text. This liquid doesn’t combust on a hot day, but storing it far from any flammable sources and oxidizers cuts down risk.
Respecting Real-World Storage Needs
No warehouse exists inside a vacuum. Temperature and humidity shift by the hour. I once watched a drum of specialty chemicals bulge because someone slid it near a heating vent, forgetting how cardboard shims hold heat. N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate calls for tight seals and containers made from glass or specific polymers. Keep it cool—room temperature suits just fine—and out of direct sunlight. Too much warmth or stray moisture can set off slow reactions, or weaken seals, leading to leaks nobody wants to clean up.
Chemicals soaked up by cardboard, wood, or porous bits spread their mess, so that old habit of storing drums on pallets and away from drains proves worth it time and time again. Labels should stay crisp and visible—can’t count how often faded markers or missing tags create confusion.
Staying One Step Ahead When Handling
Every safe handling routine I’ve seen boils down to habit. Gloves—nitrile beats latex—keeps skin safe. Splash goggles dodge surprises from splatter. Chemical aprons or lab coats, though unpopular in summer, stop spills from reaching you. Simple tools like those squeeze-wash bottles, eye showers, and spill kits close by give workers a fighting chance. Coughing or stinging often signals missed steps, such as not washing after handling or dropping tools into containers.
Nobody wants to chase paperwork, but recording what comes in, gets used, and leaves the shelf helps head off accidental mix-ups or shortages. Good records mean no last-minute scrambles for replacements. Waste needs its own spot, away from everything else—reusing old bottles never ends well.
Look for Small Signs: Stay Vigilant, Sharpen Your Senses
It all feels like repetition until something goes wrong. Leaks, odd smells, crystallized residue—these aren’t quirks, they’re warnings. My worst days in the field involved mop-ups that traced back to skipped inspections. Every week or two, scan containers and check for cracks. If you find a problem, isolate it right away and use the right absorbents and protective gear—a single oversight can expose someone, pollute workspaces, or ruin expensive stock.
Colleagues carry most of the load. A few reminders taped to cabinets, quick safety walks, and speaking up when you see an error keep everyone honest. More than equipment or paperwork, this culture of attention and regular check-ins saves lives and jobs.
Building Better Habits—Not Just Rules
Experience, not just regulations, shapes safer labs and storerooms. Those routines—putting things back in their place, checking expiration dates, scrubbing worktops—matter more than any checklist ever could. N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate isn’t all that rare in labs these days but it commands respect, just like any chemical. Facts, old wisdom, and a steady hand: that’s what keeps teams safe.
Why Purity Matters in Everyday Products
Anyone who has tried to buy over-the-counter medicine or lab chemicals has seen purity grades listed on the bottle. These numbers and codes show how much of the product is actually the substance you’re paying for, with the rest usually being harmless fillers or trace impurities. It’s easy to overlook these values, especially if you’re not working in a lab or running a food business, but purity affects both price and performance.
During my time working in a university chemistry setting, we couldn’t cut corners with materials. Every experiment relied on reagents of known quality. A slight drop in purity could mean failed results or wasted money. Students and staff needed to trust every label. Outside the lab, people rely on those same assurances, from prescription pills to food additives.
How Purity Grades Get Decided
Grades such as “USP,” “NF,” “ACS,” or “Food Grade” refer to published standards. Each body—like the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) or the American Chemical Society (ACS)—sets its own benchmarks. For example, USP grade materials are okay for medical use, while ACS grade goes through extra screens for contaminants meant for analytical work. Labels like “Technical” grade signal lower purity and possible unknown contaminants, normally used for industrial processes where absolute clean samples aren’t needed.
Purity on the label often reads as a percentage. For sodium chloride (table salt), something listed as “99.9% ACS Reagent Grade” means you get at least 999 parts out of every 1,000 as pure salt, and only 1 part as everything else. That 0.1% matters; in electronics, even a trace element can ruin microchips. In food, an impurity may trigger allergic reactions.
Testing and Verification: No Guesswork Allowed
It’s not enough for a company to slap a grade on a product. Every batch should get checked, and those checks are only real if they’re routine. Trusted manufacturers run advanced methods like HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography), mass spectrometry, and titration. Labs compare samples against certified reference materials, often issued by national agencies such as NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology). These methods confirm both the actual purity and the levels of specific impurities, ensuring that nothing slips past unnoticed.
Many buyers—researchers, businesses—ask for a certificate of analysis (CoA) with their purchase. This document lists everything tested, the results, who tested it, and the date. If a producer refuses to provide this, red flags go up immediately for any responsible user.
Building Trust: From Maker to User
The best way to keep purity honest is transparency. I always seek out companies that don’t treat their CoA like a trade secret. If a company publishes recent test data, describes its testing labs, and lets customers ask questions, people are much more likely to trust the product. Third-party audits and international certifications add even more weight.
In the end, purity is a promise—one backed by precise methods, openness, and regular checks. Anyone buying medical additives, reagents, or supplements should check for clarity about the grade and proof behind it. This isn’t just a science problem; it affects people’s safety and money every day.
Spotlight on Chemical Controls
Moving chemicals like N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate always turns up a pile of rules and paperwork. Not every compound shows up on international watchlists, but piperidinium-based products can attract questions from customs, safety regulators, and sometimes, law enforcement.
I’ve seen the headaches shippers face when a product—especially one that’s rare or mostly used in labs—gets flagged for extra scrutiny. Look up this salt in chemical inventories and it won’t always jump out as something strictly prohibited, but that doesn’t mean it glides through every border. The structure, part of the quaternary ammonium salt group, could set off alarms in places rolling out tight precursor laws. Put simply, anyone involved in the supply chain, from manufacturer to freight handler, needs to watch for ever-changing global and regional lists.
Why Regulations Shape Shipments
Rules exist for good reasons. Some piperidinium compounds show up in pharmaceutical research and battery electrolytes, but this family has also hit headlines for the wrong reasons, tied to misuse and synthesis of drugs. That reputation means even legitimate orders of N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate might get flagged or delayed as authorities try to weed out illegal shipments.
I remember colleagues who thought sending one bottle by air was the same as mailing a book. Next thing they knew, customs had split the shipment open, chemical bottles lined up on stainless steel tables, phone ringing all day with compliance teams asking for extra documentation. Even if you show lab purchase orders, getting stuck in a gray legal area wastes time and money. Shipments that get held up lose a lab weeks of work and eat into supply contracts.
Classification is Key
The hazard profile for N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate deserves attention. It doesn’t swell up on flammable lists like ethers or acetone, but chemical safety data sheets stress the need for proper labeling and packaging. In EU countries, the REACH regulation controls new and unusual compounds. In the US, the DEA and Department of Homeland Security might investigate piperidine salts if there’s a hint of diversion risk. China and other Asian hubs demand clear labeling and import documentation.
Mix-ups between trade names and chemical names can cause trouble. Using proper CAS numbers cuts down on confusion. I’ve walked into old stockrooms where the same shelf stored “Piperidinium acetate” from one supplier and “N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate” from another—no cross-references, no clarity. That ignorance costs in surprise inspections or possible legal violations.
Balancing Access and Security
Getting N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Acetate from the supplier to the warehouse safely means balancing researcher needs with security concerns. Companies that thrive in this sector build relationships with customs brokers and stay up to date on monitoring programs. Training logistics staff on recognition of hazardous materials and staying in touch with compliance officers keeps things moving.
To keep delays down, careful documentation and transparent records matter. Companies able to track their chemicals from source to client, and contribute to chemical stewardship discussions, usually sail through reviews faster. Labs and shippers who stay one step ahead of evolving regulations carve out a real edge, while those who treat every package like low-priority cargo keep running into roadblocks.