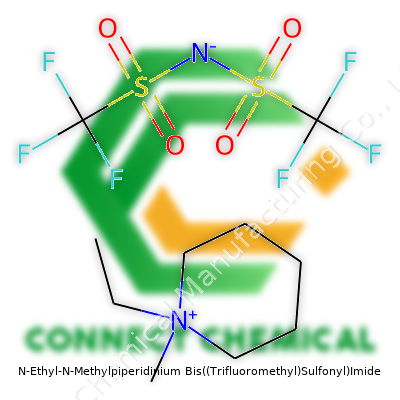
N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Bis((Trifluoromethyl)Sulfonyl)Imide: A Deep Dive
Historical Development
Decades back, the search for efficient electrolytes led scientists into the realm of ionic liquids, and not many caught as much attention as N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Bis((Trifluoromethyl)Sulfonyl)Imide. Early work around the 1990s concentrated on synthesizing stable, non-volatile compounds for battery applications. Researchers in Europe and Japan took charge, exploring different cation-anion combinations to push thermal and electrochemical stability to new heights. The spread of research papers accelerated after the turn of the century, as high-profile failures of organic electrolytes steered funding agencies toward this class. This particular salt emerged as a favorite for its balance of conductivity, low toxicity profile, and resistance to hydrolysis.
Product Overview
N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Bis((Trifluoromethyl)Sulfonyl)Imide now occupies a key spot in specialty chemicals. This compound is a colorless to pale yellow liquid at room temperature, known for its negligible vapor pressure and impressive electrical properties. Many commercial forms come as highly pure liquids, free from halides, making them suitable for direct use in sensitive electrochemical cells. The high price tag on this product stems largely from its demanding synthesis and purification process, alongside its low-volume, specialized market.
Physical & Chemical Properties
With a melting point generally below room temperature, N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Bis((Trifluoromethyl)Sulfonyl)Imide stands out among ionic salts. The viscosity runs higher than water but is manageable for most lab procedures. Its colorless nature and faint odor reflect a high level of purity. The molecular structure ensures high ionic conductivity, often reaching values above 7 mS/cm. Hydrophobic properties, brought by the bis(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)imide anion, allow use in moisture-prone applications where hydrolysis presents a risk. Electrochemical stability windows stretch from below 0 V up to over 4.5 V versus Li/Li+, making it compatible with lithium-based batteries and high-voltage supercapacitors.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Producers measure water content using Karl Fischer titration, reporting values under 20 ppm for best-grade lots. Heavy metal impurities—often controlled to below 1 ppm—show the attention to detail during manufacturing. Solubility profiles, especially in acetonitrile, propylene carbonate, and similar solvents, get detailed on product labels. Labels emphasize sensitivity to air and recommend nitrogen-blanketed storage. Batch numbers and certificates of analysis guarantee traceability, which becomes vital in regulated industries.
Preparation Method
Most syntheses start with piperidine derivatives, allowing careful alkylation to introduce ethyl and methyl groups. During the next stage, the piperidinium salt converts through metathesis, replacing halide ions with bis((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)imide. Purification follows, using multiple washings and extractions to drive down residual halide and water content. Every detail counts here, since minor impurities often tank electrochemical performance. Walk into a well-run synthesis lab, and you’ll see technicians handling dry boxes and Schlenk lines to avoid moisture pickup at every step.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
Once in hand, this ionic liquid rarely reacts unless pushed with strong nucleophiles or oxidants. Under rigorous testing, the piperidinium core holds up against hydrolysis and reduction. Scientists have experimented with swapping out the imide anion or adding alkyl chains to the piperidinium ring, which can tune viscosity and electrochemical window. Advances in functionalized versions of the molecule—for example, introducing side chains for self-assembling films—have broadened potential uses.
Synonyms & Product Names
Depending on supplier and context, the chemical often appears under these names: N-ethyl-N-methylpiperidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide, 1-ethyl-1-methylpiperidinium TFSI, or simply EMPipTFSI. The acronym TFSI turns up in most technical documentation, reflecting the legacy name for the anion.
Safety & Operational Standards
Handling this compound demands familiarity with glovebox or at least glovebag techniques to cut down risk of accidental moisture contamination. Most guidelines stress the use of chemical-resistant gloves, eye protection, and splash-proof lab coats. Although acute toxicity sits low compared with legacy solvents, spills need immediate cleanup since fluorinated compounds resist easy breakdown. Disposal routes pass through high-temperature incineration, not down the drain. Laboratories keep this salt locked in desiccated cabinets, often under inert gas. Regular audits ensure compliance with workplace exposure limits, even though few problems have emerged from long-term use.
Application Area
You’ll find N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Bis((Trifluoromethyl)Sulfonyl)Imide in development labs targeting next-generation batteries, especially those demanding safety in rugged environments. Makers of supercapacitors value it for its broad electrochemical stability and negligible volatility, a combo that helps prevent device failure over long term cycling. It turns up in physical organic labs exploring new fuel cells and even as an antistatic additive in polymer processing. Some developers run experiments using this ionic liquid as a solvent for organometallic catalysis, attracted by its ability to dissolve both polar and nonpolar species without decomposing under mild heating.
Research & Development
Progress in electric vehicles and grid storage keeps demand for robust, thermally stable ionic liquids growing every year. Academic labs explore blends with lithium salts and other room-temperature ionic liquids to boost conductivity and lower cost. Industry partnerships with universities focus on improving scalability of the synthesis, aiming for routes that balance cost, purity, and overall yield. Every year, new patent filings propose tweaks to the ring structure or anion, chasing incremental improvements in performance or safety. Especially since the boom in renewable power storage, interest in this class of electrolytes shows no sign of cooling.
Toxicity Research
Compared with many commercial solvents and some early ionic liquids, N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Bis((Trifluoromethyl)Sulfonyl)Imide scores favorably. Peer-reviewed studies on aquatic and mammalian models suggest only mild acute toxicity, though chronic effects remain under study. Regulatory agencies like ECHA and EPA track new data closely, particularly breakdown products after long-term use in batteries or industrial settings. Labs have looked for evidence of endocrine disruption or accumulation; so far, the molecular structure tends to resist easy biological uptake, reducing risk. Industry efforts to increase transparency now require full SDS sheets, clear labeling, and proper hazard communication, supporting safe lab and commercial handling.
Future Prospects
With the world shifting toward decarbonized energy, the hunger for stable, high-performance electrolytes will only grow. Researchers target cost and sustainability, investing in greener synthesis methods and recycling routes to recover value from spent batteries. Direct application in batteries, supercapacitors, and advanced coatings already leads to real-world products, not just academic curiosity. Changes to environmental regulations may drive demand for ionic liquids featuring lower fluorine content or increased biodegradability. Companies exploring electric flight or large-scale storage see compounds like this one as the backbone of safer, more reliable systems. My years working with specialty chemicals taught me that the pace of improvement can surprise — and it’s clear no lab or company working on next-generation electrochemistry ignores this class of materials anymore.
What Sets This Compound Apart
You don't usually find people chatting about N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Bis((Trifluoromethyl)Sulfonyl)Imide over coffee. Still, more folks should care, especially given the shifting landscape of energy storage and green technology. The name might belong in a spelling bee, but the benefits don’t hide behind jargon. In labs and workshops, this compound shows up as a special kind of ionic liquid, a category famous for their liquid state at room temperature, low volatility, and impressive stability. For anyone with sweaty palms over battery leaks or toxic byproducts, these features can mean safer products at home and in industry.
Touching Modern Tech in Quiet Ways
Big battery investments are happening worldwide, from cities scrambling to stabilize renewables to folks looking for longer phone and laptop runtime. In these batteries, ionic liquids like this one start to look very attractive. Lithium-ion batteries—the ones inside so much of our tech—sometimes catch fire or struggle as temperatures swing. Traditional liquid electrolytes catch some blame. Here’s where compounds like N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Bis((Trifluoromethyl)Sulfonyl)Imide come in. They can replace old solvents with a material that won’t vaporize or ignite under stress, which brings peace of mind and insurance savings.
These ionic liquids help pull more mileage out of batteries by resisting breakdown, so devices last longer before wear and tear catches up. That means fewer dead batteries filling up recycling bins and less waste for everyone. That’s not just good science, that's solid living. Data shows the electronic waste pile hit 53.6 million metric tons in 2019, according to the United Nations. Any step, even a chemical tweak, that stretches battery life, brings real gains at home and on the planet.
Factoring in Industrial Demand
Industries don’t just covet longer battery life. Some turn to ionic liquids as solvents for tough chemical processes, because these don't boil or break down near as easily as many traditional fluids. This boosts efficiency for electroplating or pharmaceutical synthesis, where every hiccup costs time and money. N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Bis((Trifluoromethyl)Sulfonyl)Imide, with its stability and conductivity, lets manufacturers try reactions that older solvents couldn’t handle without toxic byproducts.
Just last year, more research papers started exploring these ionic liquids in advanced applications, from flow batteries to carbon capture. People in the field talk about them not just for what they can do, but for the doors they could open to cleaner chemistry down the road. There's still a cost hurdle—creating these compounds isn’t cheap, and that slows how fast they’ll show up in every car battery or factory floor. But with the right research funding, the production process may soon get easier and less expensive.
Next Steps for Safer and Greener Chemistry
Relying less on hazardous chemicals and moving toward stable, safe alternatives does more than just help industry. It means cleaner manufacturing, fewer accidents, and a lighter footprint on the world. Groups seeking ways to drive down the price of safe ionic liquids will need to collaborate—engineers, government labs, manufacturers, and investors pulling together should keep pushing improvements in chemistry that show up in everyday goods.
Every time I see another device last a year longer or a company cut accident rates, I remember that no scientific leap stands on its own. Behind complicated names sit stories of real progress. As materials like N-Ethyl-N-Methylpiperidinium Bis((Trifluoromethyl)Sulfonyl)Imide edge into the mainstream, the real win is safer tech that doesn't keep us up at night.
Real Questions Start with Structure
Every time someone asks about the formula or structure of a chemical compound, it brings me back to university chemistry labs. My own hands trembled more than once pipetting unfamiliar liquids, but nothing compared to the uncertainty brewing in my mind about what was actually happening inside the flask. Knowing just a chemical formula doesn’t give the full picture. The structure—how those atoms are arranged and bonded—holds the key to understanding what the compound can do or what risk it poses.
Take water: H2O. Easy enough to recite in grade school, but the story builds in organic chemistry. Glucose, for example, goes by C6H12O6. Each letter and number hints at the building blocks, but it suggests nothing about the compound’s energy storage capacity or its chirality. Changing the layout turns sweet glucose into bitter mannose. So structure isn’t some academic curiosity; it decides taste, toxicity, and utility.
Formula: More Than Numbers
Recognizing a chemical formula is like glancing at blueprints. No architect stops at “four walls and a roof,” and chemists don't stop at the letters and subscripts. With sodium chloride (NaCl), you get table salt—a crystal lattice gluing sodium and chlorine together through ionic bonds. The tight grip between the ions explains salt’s high melting point and its way of drawing moisture.
In my experience teaching high school science, simple formulas let students dip their toes into chemistry, but real science lives in the connections. Penicillin, for example, includes a β-lactam ring—a structure that lets the drug stop bacteria from building cell walls. Mess with the bond angle or swap one chemical group, and the medicine stops working. It’s not just the atoms; it’s how they’re glued together.
Why This Matters—And Where Trouble Grows
Chemical structures drive everything from drug development to food safety. Acetaminophen and phenacetin share a backbone, but minute changes make one a handy fever-fixer and the other a banned substance linked to cancer. Small kids, like my niece with peanut allergies, depend on detailed structural information. One misplaced hydrogen might mean anaphylaxis rather than a harmless snack.
Looking back, so many chemical spills or accidental poisonings stem from misunderstanding structure. It’s not enough to store bottles labeled “C6H12O6” or “C2H5OH”—industry and education both must keep diagrams and hazard information in view. Knowing what benzene looks like—a flat ring, with delocalized electrons—explains both its use in plastics and its cancer risk. In rural towns, folks handling farm chemicals rely on trustworthy, visual information and clear labeling to avoid confusion between safe fertilizers and risky pesticides.
Pushing Toward Solutions
In my work as a science communicator, plain language and visual aids bridge the gap. Instead of scattering cryptic formulas on labels and safety sheets, real-world diagrams and succinct explanations help everyone from kids to seniors recognize dangers and benefits. Quick-response codes on bottles, linking to verified descriptions and images, harness today’s tech to build trust and safety.
Science grows fast, but clarity remains timeless. Rooting formulas in real, tangible structure and context keeps communities safer, training sharper, and curiosity alive in the next generation of chemists.
Why Proper Storage Matters
Good storage practices often get ignored until something goes wrong. Years of working in warehouses and handling deliveries taught me that careless storage causes more trouble than any shipping delay ever could. From spoiled food to unpredictable chemicals, the right storage stops accidents, spoilage, and expensive losses. Products with sensitive ingredients often react quickly to moisture, air, heat, or cold. That means ignoring a “keep dry” or “do not freeze” warning leads straight to complaints, recalls, and insurance claims nobody wants.
Temperature: Not Too Hot or Too Cold
Most products want a steady, moderate temperature—nothing fancy, just not too extreme either way. Medicines, food, and chemicals: these categories all come with their own temperature sweet spots. Over several summers, I saw how a warehouse without air conditioning lets heat creep up, turning cartons into soggy lumps or causing bottles to burst. On the flip side, some products don’t handle the cold well—a couple nights of hard freeze ruins an entire shipment. The consequences pile up fast: loss of value, health and safety risks, and long arguments with suppliers.
Moisture Control and Cleanliness
Humidity sneaks in from leaky roofs, open doors, or even careless transfers from trucks to storage racks. A dry environment makes a huge difference. Cardboard breaks down, powders clump, and sensitive materials pick up moisture much faster than most people realize. My years in retail taught me to obsess over spills, leaks, and even the grit that comes from dusty pallets. Keeping a clean, dry space isn’t just old-fashioned advice—it keeps products ready for customers and compliant with regulations.
Safe Handling: Reduce Accidents, Protect People
Handling isn’t only about boxes and forklifts. People also need personal protective equipment, good lighting, and enough training to spot problems before they get out of hand. Gloves, goggles, and safe walking lanes aren’t just for show. Staff who don’t get rushed or overwhelmed tend to catch leaks, strange smells, or broken packaging early on, which stops bigger problems. Clear labeling and proper stacking help prevent mix-ups, protect against falls, and make inventory checks easier.
Security and Traceability
Security often gets overlooked in a quiet storage room, but product theft and tampering cost more than most business owners think. Keeping storage locked, limiting access, and logging inventory movement deal with this risk head-on. Logging isn’t only for audits—track what comes in, goes out, and what sits on the shelf too long. If a recall ever hits, traceability cuts down stress and cost by showing exactly where everything went.
Smart Solutions: Technology and Training
Adopting sensors for temperature and humidity pays off with early warnings. Lightweight tracking tools, even just barcode scanners, speed up work and cut down on mistakes. Investing in staff pays off more than any fancy security camera: regular training sessions turn nervous newcomers into rock-solid crew members. That doesn’t cost much and keeps everyone safer.
Experience taught me that spending a little time and money to set up the right environment saves a lot of trouble down the road. Regulations keep changing, but keeping storage dry, secure, and well-run stays the smart choice—no matter what’s on the shelf.
What Makes a Product Hazardous or Toxic?
Some products in the home or workplace do more harm than good when used carelessly. Take bleach as an example. Most folks use it for cleaning, but mixing it with ammonia or acids releases toxic gases. Respiratory trouble sets in fast from these fumes. Even everyday things like certain paints, adhesives, and cleaners can have solvents that affect your health. Long-term exposure to household chemicals, like those found in air fresheners or nail polish removers, sometimes links to headaches or dizziness.
Hazardous and toxic labels don’t just cover industrial chemicals. Look under your kitchen sink or in the garage. Bleach, antifreeze, drain cleaners, pesticides—these are risky. A surprising number of kids end up in the ER every year because of these products. The American Association of Poison Control Centers reports that household cleaners were among the top substances involved in their calls in recent years. Inhaling vapors or getting liquids on the skin is enough to spark a chemical reaction, sometimes without warning.
Why It Matters for Everyday Living
People trust that store-bought things are safe, but that’s not always the case. Manufacturers print instructions and symbols for a reason. Products often have warnings you’ll miss if you’re in a hurry—a flammable icon, a caution for skin contact, statements against mixing with other brands or chemicals. Every year, forgotten precautions lead to burns, poisons, or fires. Even something as familiar as bug spray can bring trouble indoors if you lose track of ventilation or proximity to food.
In my own experience, ignoring those warning labels led to an itchy rash after using a garden weed killer. I washed with bare hands, forgetting gloves. That minor decision took a week to heal. The point is, risk comes not from the tools themselves but from choices people make around them. A quick skim of instructions or a glance at a Material Safety Data Sheet reveals a lot—not just ingredients but also what to do in an emergency.
Practical Steps to Lower Your Risk
Simple habits make the biggest difference. Always wear gloves, a mask, and eye protection with harsh chemicals or sprays. Good airflow reduces what you breathe in—open windows or use a fan. Store chemicals high and out of reach if there are children or pets. Return lids tightly after each use to prevent spills or accidental exposure.
Never mix cleaning products unless you’re sure they’re meant for it. Take extra care with acids and alkalis; combining them sometimes leads to dangerous compounds. Older adults and young children have weaker immune systems, so even tiny spills can matter. For anyone with asthma, stick to low-odor and “green” cleaner options and steer clear of strong scents.
Disposal matters too. Tossing old paint or pesticides in the trash pollutes water and affects wildlife. Many towns offer hazardous waste collection events. Call your local waste service to find drop-off spots. Always read the disposal section of the product label before throwing anything out.
Knowledge and Caution Go Hand in Hand
Hazards follow misuse more often than malfunction. Reading up on what a substance really does and what health professionals report sharpens your judgment and keeps families safe. No one can watch every health risk, but for the products people buy and use every day, a little care goes a long way.
Everyday Chemistry: Purity Means More Than Numbers
Most people outside the lab might not think about what goes into a bag of chemicals. For people working with these products—whether in a pharmacy, factory, or research lab—the purity figures printed on a label tell a big part of the story. 99% might look good at a glance, but those other decimal points can make or break an experiment or batch. Most standard chemicals are supplied at purities from 97% up to 99.9%, with a special grade called "ACS Reagent" or "Analytical Reagent" commonly reaching 99.5% or more. Industries tied to electronics or pharmaceuticals frequently need “ultra-high purity,” which can reach as high as 99.999% for sensitive applications.
Working with chemicals means knowing the true nature of what’s in your hands. Even trace contaminants—just one in a thousand—can ruin a sensitive reaction or introduce safety hazards, especially in drug production or microchip fabrication. I’ve seen researchers struggle for weeks, only to discover a batch of “pure” solvent contained a harmless-seeming but stubborn contaminant, changing their results.
Packaging: From Bench to Tonne
Chemical companies don’t take a one-size-fits-all approach to packaging. On the research side, I’ve usually ordered bottles or jars ranging from 100 grams to a kilo, sometimes as little as 25 grams when working with expensive or hazardous materials. Glass jars or high-density polyethylene containers keep out moisture and light. Lab suppliers offer secure, tamper-evident seals, protecting the contents during shipping.
Industrial buyers go bigger. Chemical drums holding 25 to 50 kilograms and even 200-liter barrels arrive on wood pallets. For massive operations—think agriculture or mining—bulk containers called IBC totes hold up to 1000 liters. I remember seeing forklifts moving shrouded white totes around a chemical plant, and realizing this physical scale is part of what keeps prices low for tailored solutions in manufacturing.
Transparency and Trust
Companies trying to cut corners with impurities or mislabeled packages risk big consequences, both for safety and reputation. That’s where standards like ISO certification or adherence to the United States Pharmacopeia come in. Labs and factories demand certificates of analysis with every shipment. This practice stems from experience: after a contamination scare or bad batch, people don’t just trust what’s written on the bag. They want paperwork and often run their own spot-checks. I've had to run secondary purity tests when I suspected an anomaly—it's time-consuming, but sometimes necessary.
Building Better Access and Accountability
Pricing and access to smaller packaging still create headaches for startups and small labs. Jars priced for research can cost many times more per gram than industrial drums, limiting access for those with tight budgets. A practical step: encourage partnerships among labs to share or split large containers. Regulatory hurdles, especially for controlled substances, keep some chemicals in short supply or with high markups. The industry could help by expanding regional storage hubs and supporting reuse of safe, refillable containers, easing logistics and reducing costs.
Getting chemical purity and packaging right isn’t just a technical detail; it impacts science, safety, and how far innovation can spread. Careful sourcing, honest labeling, and better supply models would help open up the benefits of skilled chemical handling to more people and places.